Introduction to Java IO
The Java Input Output (IO) API enables Java programs to read data from and write data to file system or disk and to other devices through a network connection. The Java I/O API was introduced in the initial version of Java in the mid-90s. In Java SE 1.4, Java NIO was introduced. NIO stands for Non-blocking Input Output. In Java SE 7, NIO2 was released which is basically an improvement of the initial version of NIO.
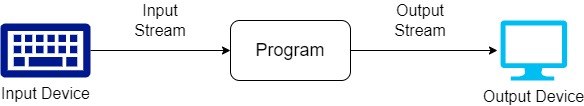
The package for Java I/O API is java.io. The package for NIO is java.nio and the package for NIO2 is java.nio.file. Java uses the concept of streams for handling input and output. A stream is a collection of data or a flow of data. Reading data from an input source requires an input stream and writing data to a target requires an output stream. These streams can be visualized as shown in below figure:
Text and Binary IO
The Java I/O API defines two kinds of content for a resource:
- Character or textual content (ex: text, XML, JSON)
- Byte or binary content (ex: image, video)
The base classes related to character streams are Reader and Writer. The base classes related to byte or binary streams are InputStream and OutputStream.
The differences between character streams and byte streams in Java are given below:
| Character Stream | Byte Stream |
| For reading or writing characters to text-based files like XML, HTML, JSON etc. | For reading or writing bytes to files like images, videos or files in low-level formats like .exe, .obj, .class, etc. |
| Deals with 16-bit Unicode characters | Deals with bytes (8-bit data) |
| Streams are called as readers and writers | Streams are called as input streams and output streams |
| Abstract base classes are Reader and Writer | Abstract base classes are InputStream and OutputStream |
For more information, visit the following links:

Suryateja Pericherla, at present is a Research Scholar (full-time Ph.D.) in the Dept. of Computer Science & Systems Engineering at Andhra University, Visakhapatnam. Previously worked as an Associate Professor in the Dept. of CSE at Vishnu Institute of Technology, India.
He has 11+ years of teaching experience and is an individual researcher whose research interests are Cloud Computing, Internet of Things, Computer Security, Network Security and Blockchain.
He is a member of professional societies like IEEE, ACM, CSI and ISCA. He published several research papers which are indexed by SCIE, WoS, Scopus, Springer and others.

Leave a Reply