In this article we will learn about IoT architecture layers. There are different IoT architectures with different number of layers.
Contents
Introduction to IoT Architecture Layers
IoT architecture enables the users to see an IoT system as a whole and what are the different components in the system. Each layer in the IoT architecture has its own function. There is no single standard IoT architecture till date. So, we will look at some of the well known IoT architectures in the existing literature.
Watch this video to learn about Internet of Things architecture layers:
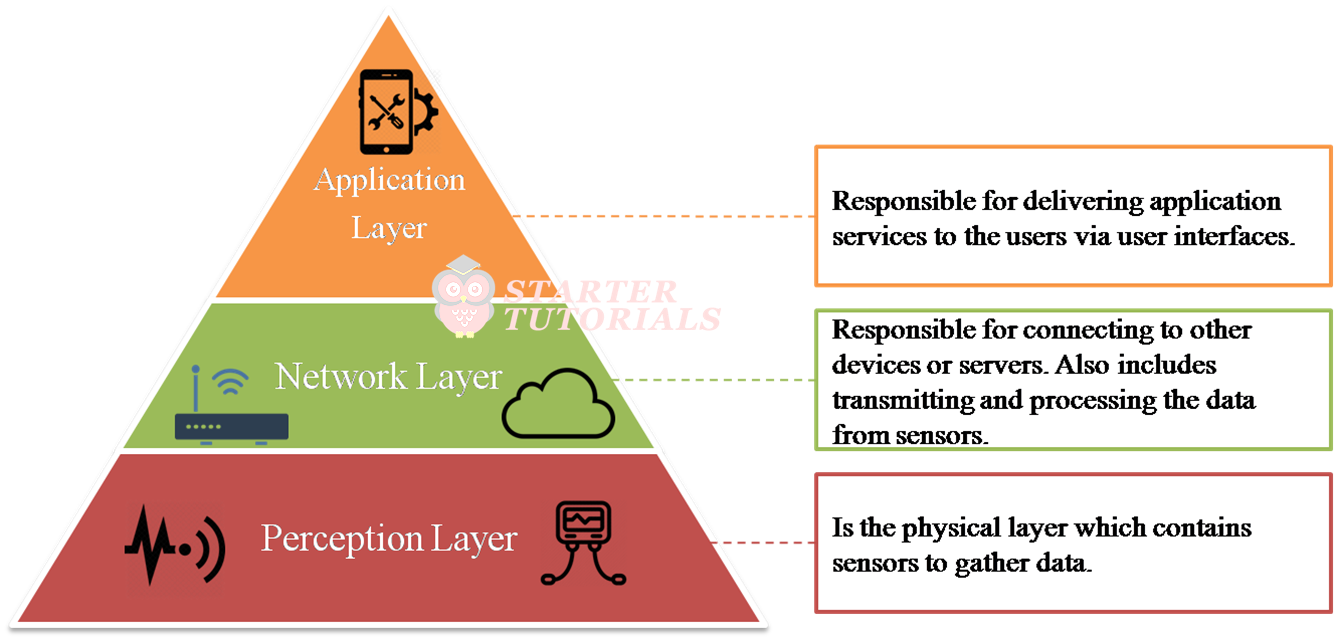
Three Layer Architecture
The layers in the three layer architecture are perception layer, network layer, and application layer.
- Perception Layer: It is the physical layer which contains sensors to gather data.
- Network Layer: Responsible for connecting to other devices or servers. Also includes transmitting and processing the data from sensors.
- Application Layer: Responsible for delivering application services to the users via user interfaces.
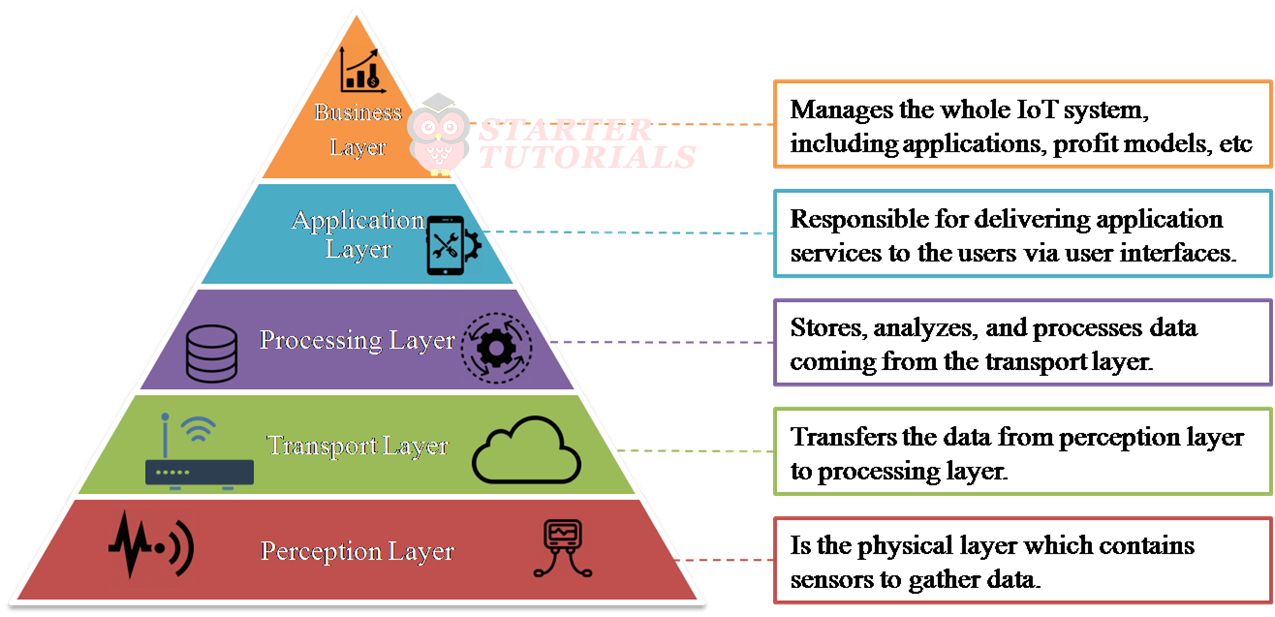
Five Layer Architecture 1
The layers in the five layer architecture are perception layer, transport layer, processing layer, application layer, and business layer.
- Perception Layer: Is the physical layer which contains sensors to gather data.
- Transport Layer: Deals with transferring the data from perception layer to processing layer.
- Processing Layer: Stores, analyzes, and processes data coming from the transport layer.
- Application Layer: Responsible for delivering application services to the users via user interfaces.
- Business Layer: Responsible for managing the whole IoT system, including applications, profit models, etc.
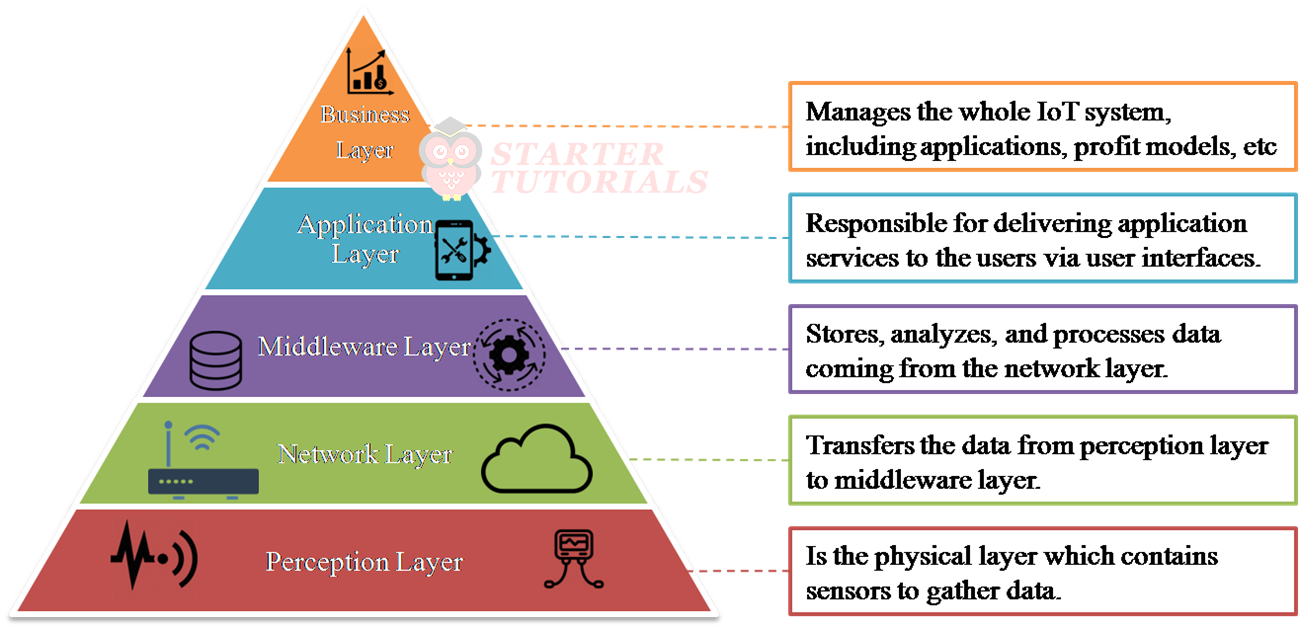
Five Layer Architecture 2
The layers in the three layer architecture are perception layer, network layer, middleware layer, application layer, and business layer.
- Perception Layer: Is the physical layer which contains sensors to gather data.
- Network Layer: Deals with transferring the data from perception layer to middleware layer.
- Middleware Layer: Stores, analyzes, and processes data coming from the network layer.
- Application Layer: Responsible for delivering application services to the users via user interfaces.
- Business Layer: Responsible for managing the whole IoT system, including applications, profit models, etc.
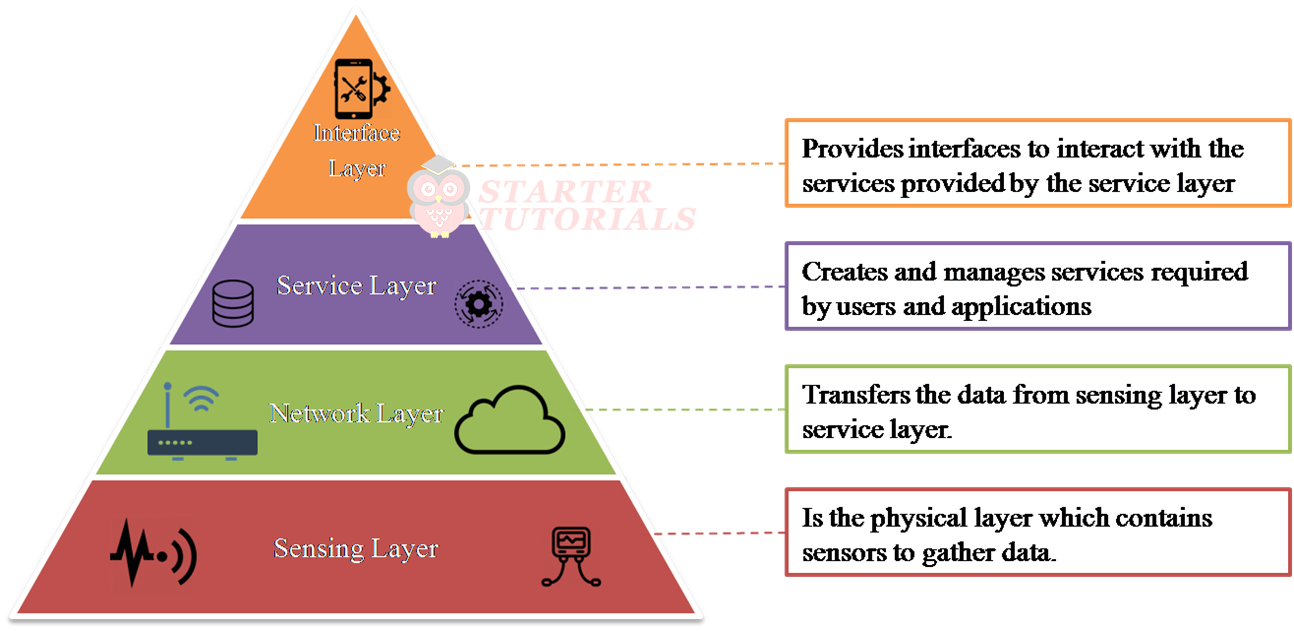
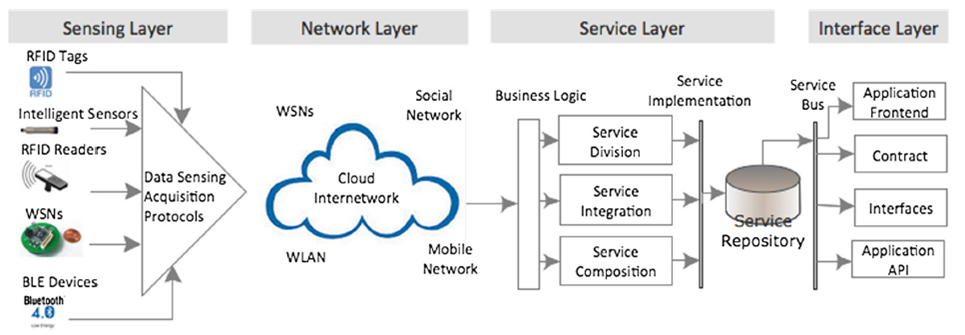
Service-oriented Architecture
The layers in the service-oriented architecture are sensing layer, network layer, service layer, and interface layer.
- Sensing Layer: Is the physical layer which contains sensors to gather data.
- Network Layer: Transfers the data from sensing layer to service layer.
- Service Layer: Creates and manages services required by users and applications.
- Interface Layer: Provides interfaces to interact with the services provided by the service layer.
The four-layer service-oriented architecture can also be represented as shown below:

Suryateja Pericherla, at present is a Research Scholar (full-time Ph.D.) in the Dept. of Computer Science & Systems Engineering at Andhra University, Visakhapatnam. Previously worked as an Associate Professor in the Dept. of CSE at Vishnu Institute of Technology, India.
He has 11+ years of teaching experience and is an individual researcher whose research interests are Cloud Computing, Internet of Things, Computer Security, Network Security and Blockchain.
He is a member of professional societies like IEEE, ACM, CSI and ISCA. He published several research papers which are indexed by SCIE, WoS, Scopus, Springer and others.

Leave a Reply