In this article we look at introduction to IoT. First we will look at a more general definition of IoT followed by a textual definition of what IoT is.
Watch this video for introduction to IoT
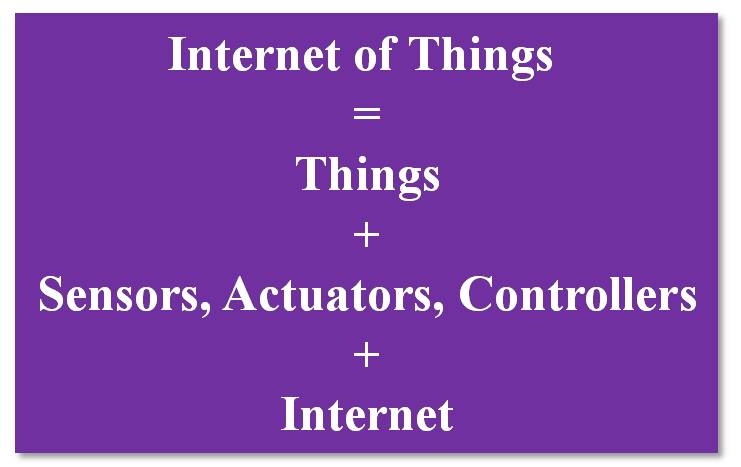
Let’s understand first about the terms Internet and a thing.
Internet: A vast global network of connected servers, computers, tablets, and mobiles that is governed by standard protocols for the connected systems.
Thing: A thing in IoT refers to physical entities or devices like sensors, actuators, and computing devices like routers, gateways, PCs, laptops, mobiles, etc.
Contents
IoT Definition 1
IoT Definition 2
Watch this video to learn about what is IoT?
The things receive inputs (using sensors) and transform them into data that is transmitted through Internet. The things also can produce output or take action using actuators.
IoT Definition 3
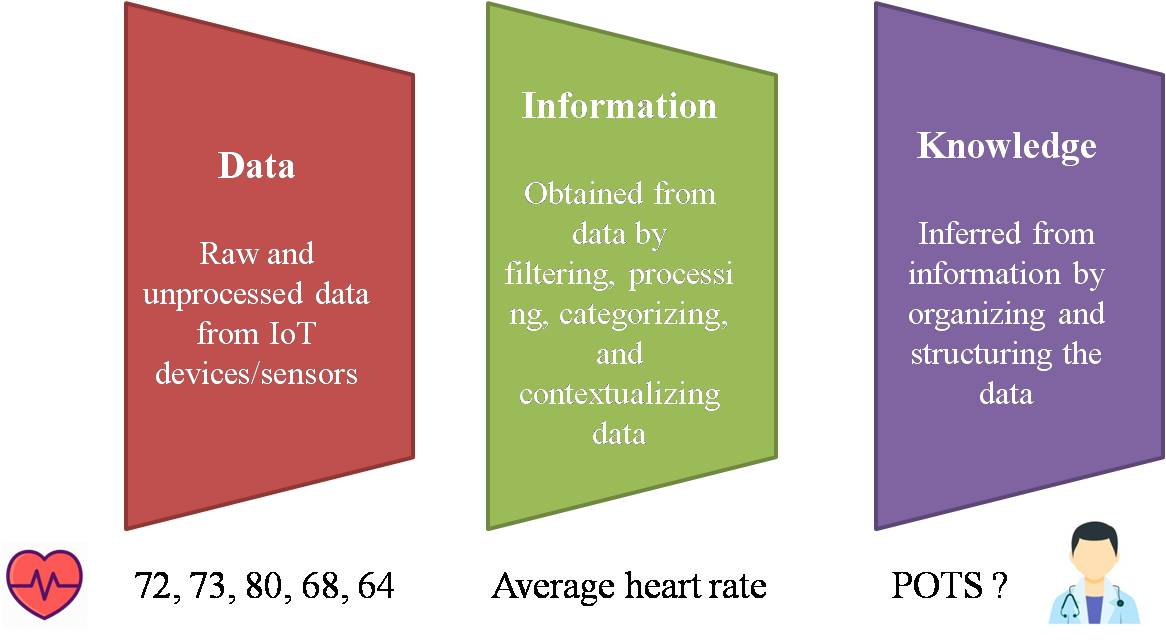
The internet of things utilizes different sensors to collect data. This data can be processed locally or in the Internet (cloud) to obtain information. Finally this information can be used to infer knowledge. This process is illustrated in the figure shown below:
In the above illustration we can see that a pulse sensor can be used to gather the pulse rate of a person. The raw pulse rate (numeric data) can be gathered 24/7 and grouped as hourly heart rate or daily heart rate. This information can be visualized as a line graph to see the trends. This information can be gathered over the years and a doctor can diagnose the person (patient) by inferring knowledge from the information collected over the months or years.
IoT Example – Internet of Streetlights
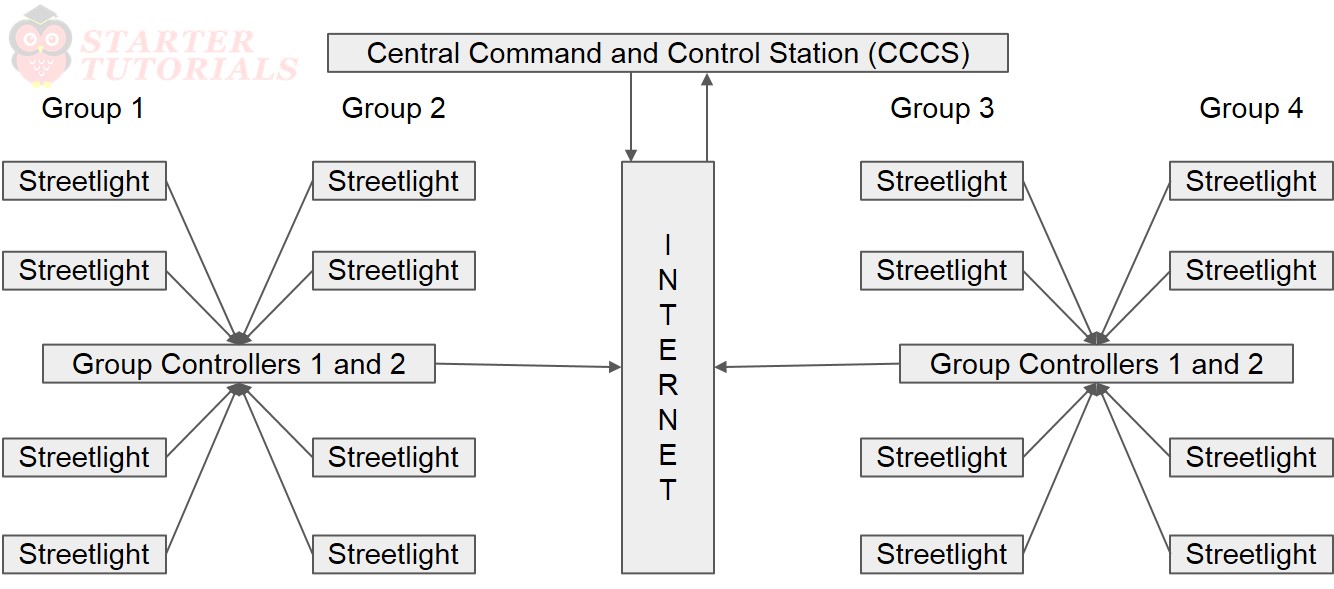
Streetlights in a city can be made to function like the lively entities through sensing and computing using the tiny edge devices (streetlights). These lights communicate and interact with a Central Control and Command Station (CCCS) through the Internet. The Internet of streetlights architecture is as shown in the figure.
Each edge device (streetlight) is comprised of sensing, computing, and communication entities. Each streetlight in a group connects to a group controller through a wireless Long Range Wide Area Network (LoRaWAN).
Each group has a communication gateway to the CCCS through the Internet. The station receives information from each group at regular intervals. The station remotely programmes the group controllers to take appropriate actions as per the traffic and lighting conditions.
Next post: Characteristics of IoT.

Suryateja Pericherla, at present is a Research Scholar (full-time Ph.D.) in the Dept. of Computer Science & Systems Engineering at Andhra University, Visakhapatnam. Previously worked as an Associate Professor in the Dept. of CSE at Vishnu Institute of Technology, India.
He has 11+ years of teaching experience and is an individual researcher whose research interests are Cloud Computing, Internet of Things, Computer Security, Network Security and Blockchain.
He is a member of professional societies like IEEE, ACM, CSI and ISCA. He published several research papers which are indexed by SCIE, WoS, Scopus, Springer and others.

Leave a Reply