Blockchain was introduced with the invention of Bitcoin in 2008. Its practical implementation then occurred in 2009. We will look at a chronological order of early history and computer networks and how they evolved and contributed to the development of Bitcoin in 2008. The order of events is:
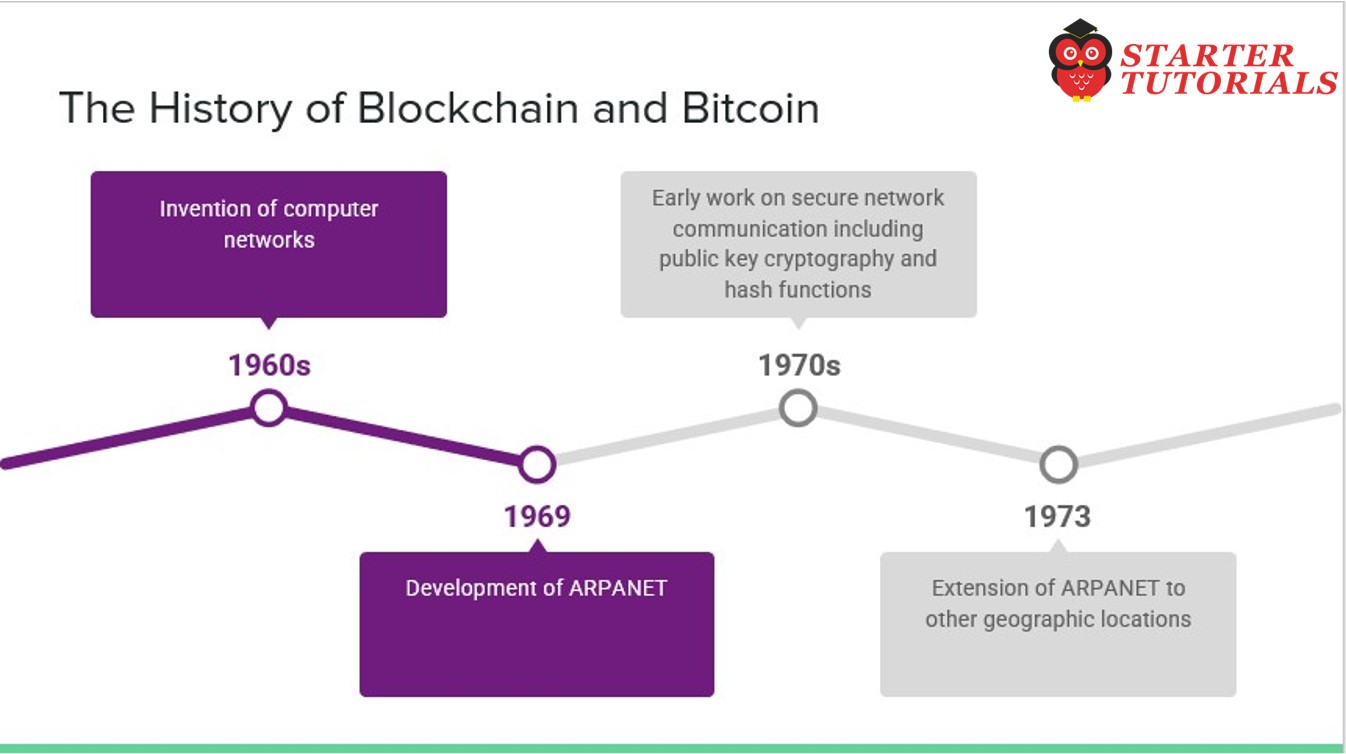
- 1960s – Invention of computer networks
- 1969 – Development of ARPANET
- 1970s – Early work on secure network communication including public key cryptography
- 1970s – Cryptographic hash functions
- 1973 – Extension of ARPANET to other geographic locations
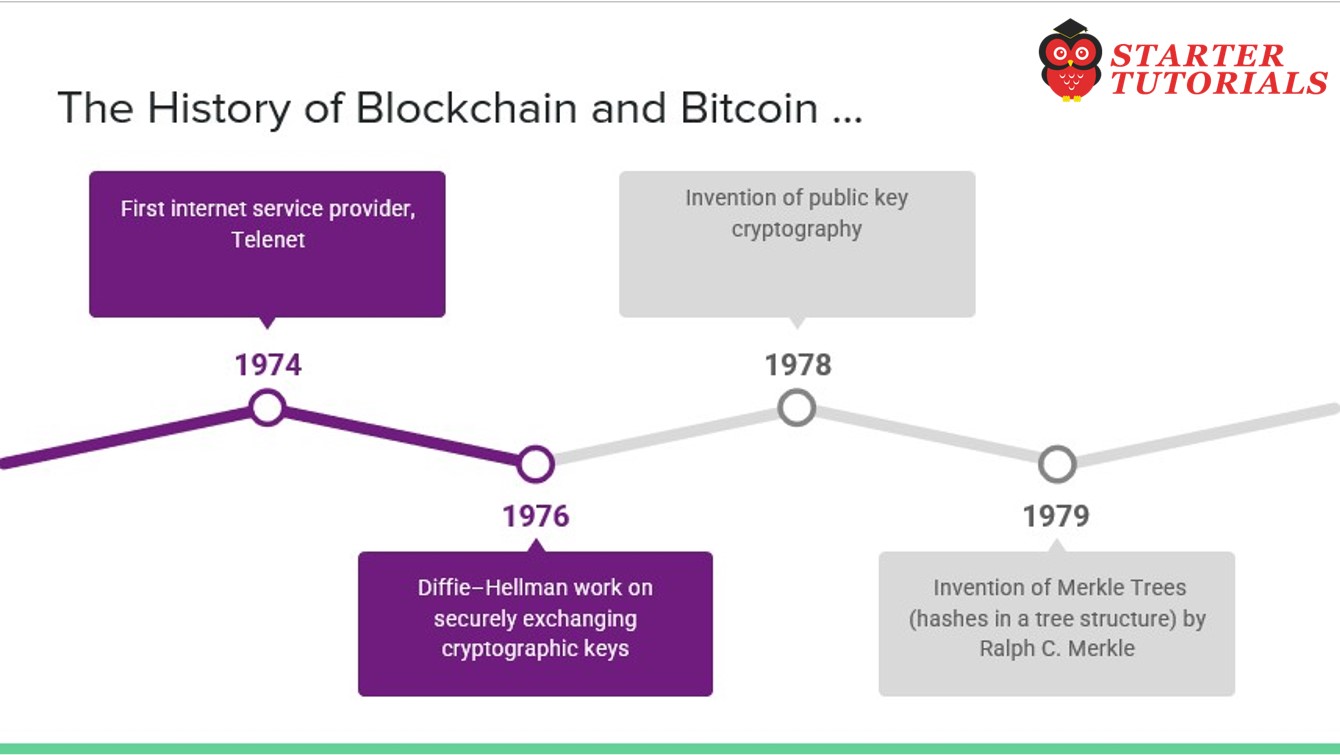
- 1974 – First internet service provider, Telenet
- 1976 – Diffie–Hellman work on securely exchanging cryptographic keys
- 1978 – Invention of public key cryptography
- 1979 – Invention of Merkle Trees (hashes in a tree structure) by Ralph C. Merkle
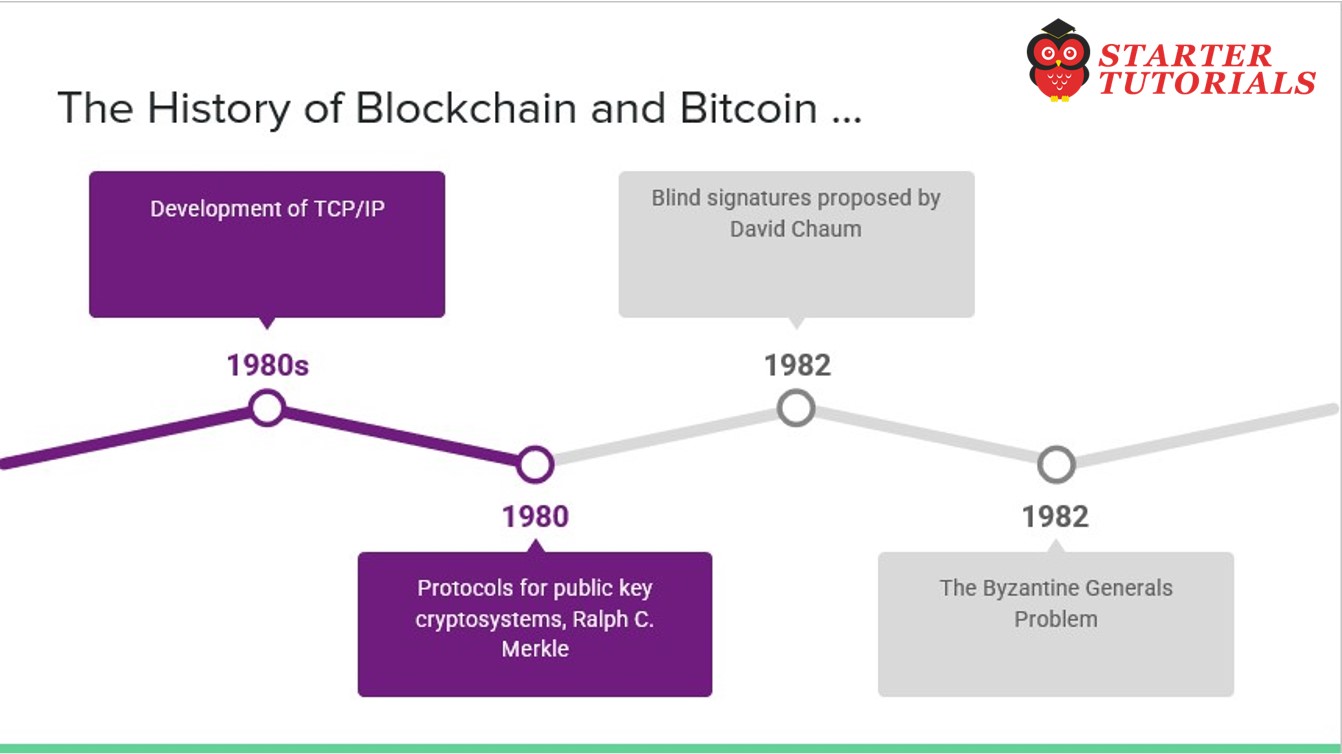
- 1980s – Development of TCP/IP
- 1980 – Protocols for public key cryptosystems, Ralph C. Merkle
- 1982 – Blind signatures proposed by David Chaum
- 1982 – The Byzantine Generals Problem (Bitcoin can be considered a solution to the Byzantine Generals Problem; however, the original intention of the Bitcoin network was to address the previously unsolved double-spending problem)
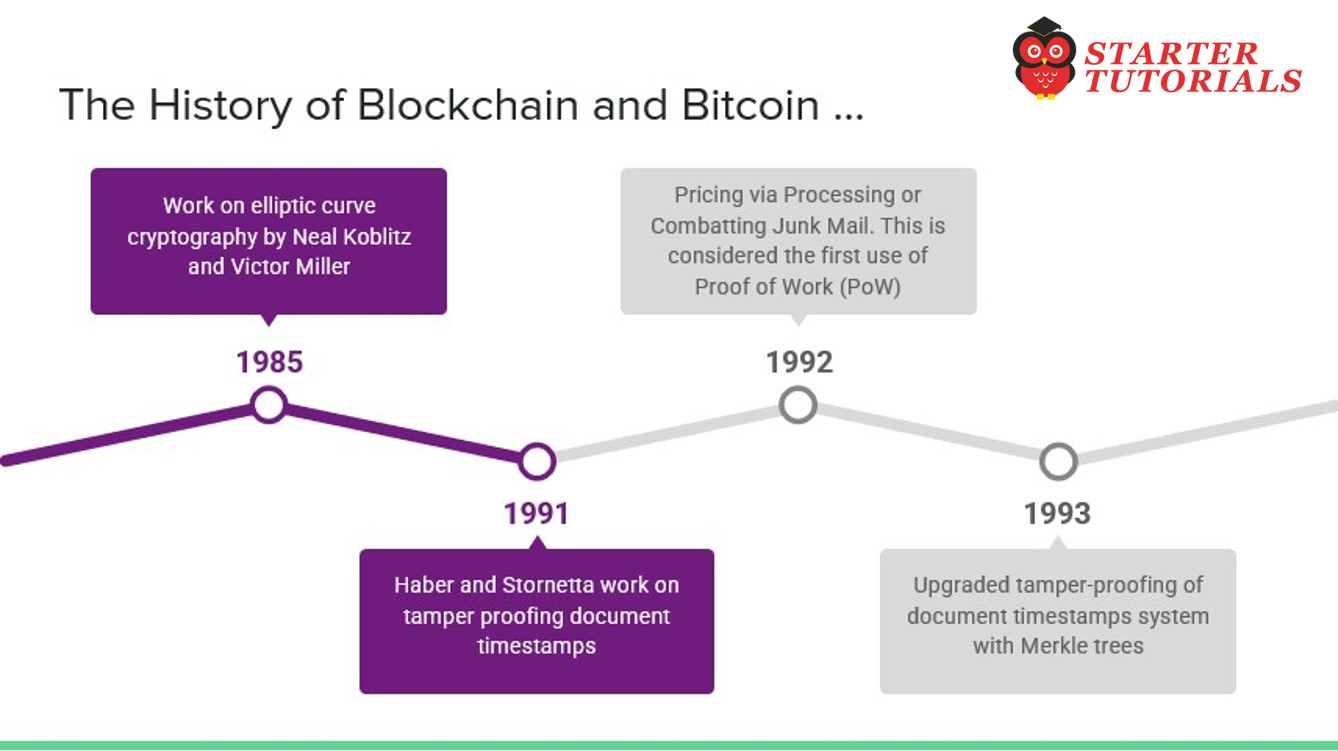
- 1985 – Work on elliptic curve cryptography by Neal Koblitz and Victor Miller
- 1991 – Haber and Stornetta work on tamper proofing document timestamps. This can be considered the earliest idea of a chain of blocks or hash chains.
- 1992 – Cynthia Dwork and Moni Naor publish Pricing via Processing or Combatting Junk Mail. This is considered the first use of Proof of Work (PoW).
- 1993 – Haber, Bayer, and Stornetta upgraded the tamper-proofing of document timestamps system with Merkle trees
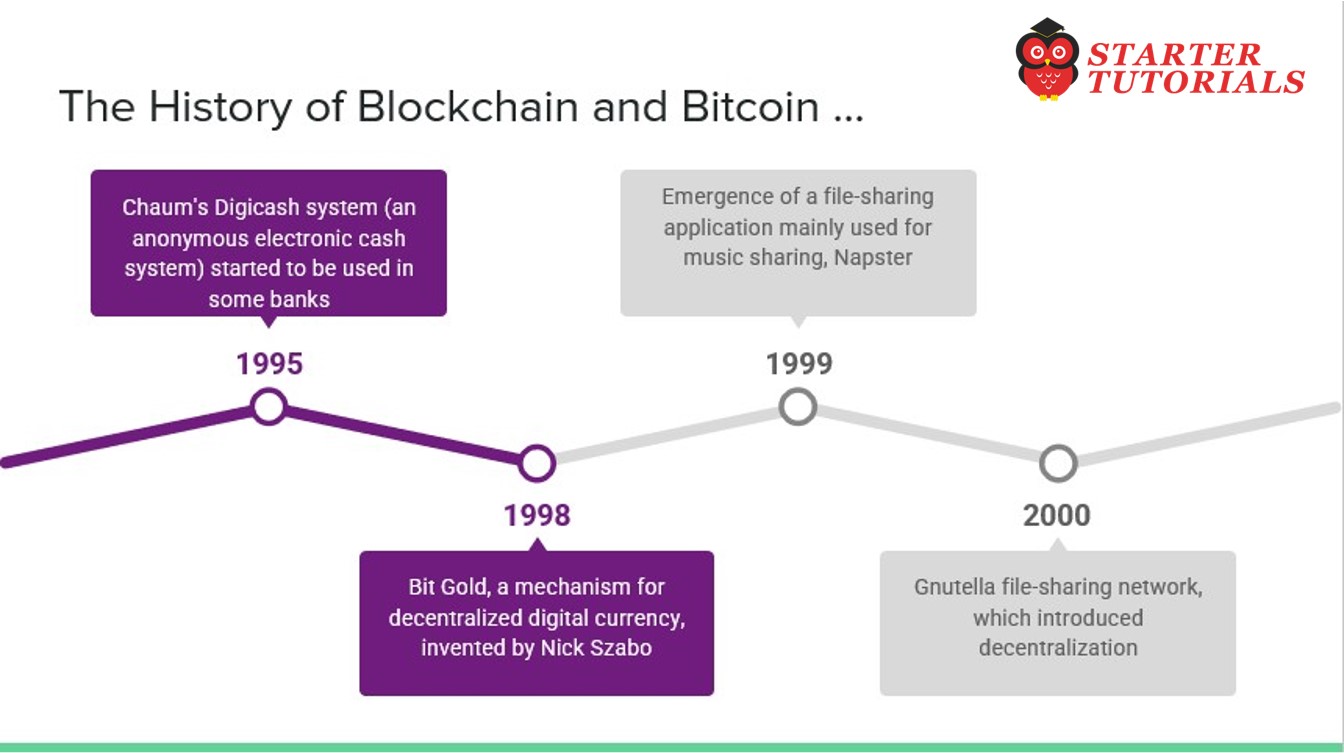
- 1995 – David Chaum’s Digicash system (an anonymous electronic cash system) started to be used in some banks
- 1998 – Bit Gold, a mechanism for decentralized digital currency, invented by Nick Szabo. It used hash chaining and Byzantine Quorums.
- 1999 – Emergence of a file-sharing application mainly used for music sharing, Napster, which is a P2P network, but was centralized with the use of indexing servers.
- 1999 – Development of a secure timestamping service for the Belgian project TIMESEC
- 2000 – Gnutella file-sharing network, which introduced decentralization
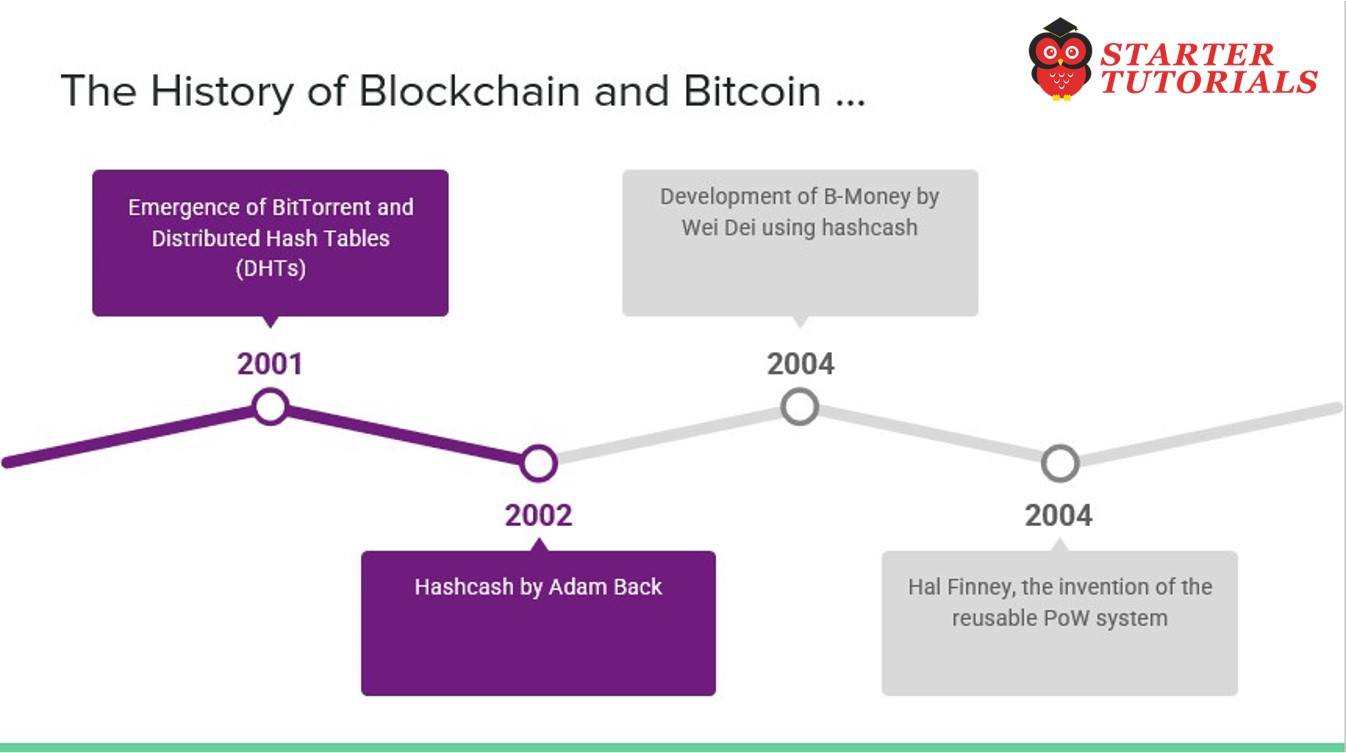
- 2001 – Emergence of BitTorrent and Distributed Hash Tables (DHTs)
- 2002 – Hashcash by Adam Back
- 2004 – Development of B-Money by Wei Dei using hashcash
- 2004 – Hal Finney, the invention of the reusable PoW system
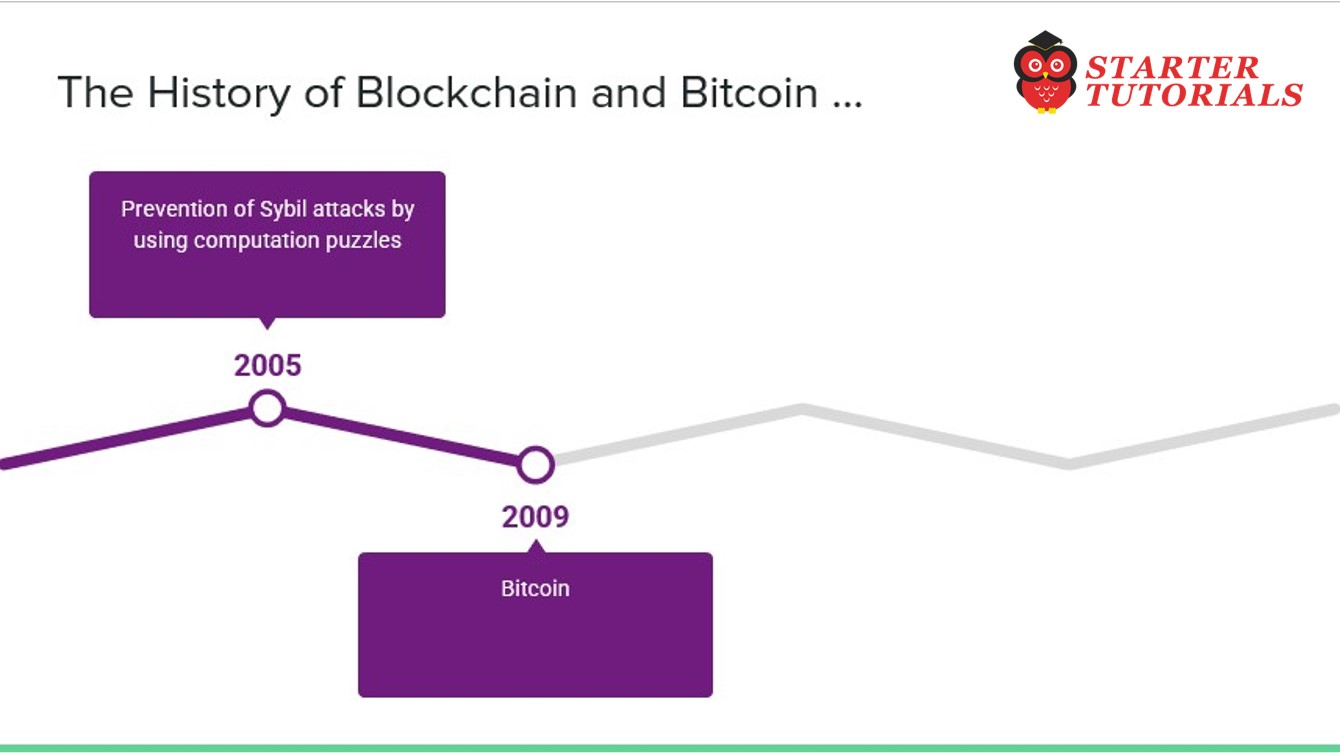
- 2005 – Prevention of Sybil attacks by using computation puzzles, due to James Aspnes et al.
- 2009 – Bitcoin (first blockchain)
All previous attempts to create anonymous and decentralized digital currency were successful to some extent, but they could not solve the problem of preventing double spending in a completely trustless or permissionless environment. This problem was finally addressed by the Bitcoin blockchain, which introduced the Bitcoin cryptocurrency.
The concept of electronic cash (e-cash), or digital currency, is not new. Since the 1980s, e-cash protocols have existed that are based on a model proposed by David Chaum. Two fundamental e-cash system issues need to be addressed: accountability and anonymity.
Accountability is required to ensure that cash is spendable only once (addressing the double spending problem) and that it can only be spent by its rightful owner. The double-spending problem arises when the same money can be spent twice.
Anonymity is required to protect users’ privacy. With physical cash, it is almost impossible to trace back spending to the individual who actually paid the money, which provides adequate privacy should the consumer choose to hide their identity.
In the digital world, however, providing such a level of privacy is difficult due to inherent personalization, tracing, and logging mechanisms in digital payment systems such as credit card payments.
David Chaum solved both of these problems during his work in the 1980s by using two cryptographic operations, namely, blind signatures and secret sharing.
Blind signatures allow for signing a document without actually seeing it, and secret sharing is a concept that enables the detection of double-spending, that is, using the same e-cash token twice.
In 2009, the first practical implementation of an e-cash system named Bitcoin appeared. The term cryptocurrency emerged later. For the very first time, it solved the problem of distributed consensus in a trustless network. It used public key cryptography with a PoW mechanism to provide a secure, controlled, and decentralized method of minting digital currency.
The key innovation was the idea of an ordered list of blocks composed of transactions which is cryptographically secured by the PoW mechanism to prevent double-spending in a trustless environment.
Other technologies used in Bitcoin, but which existed before its invention, include Merkle trees, hash functions, and hash chains.

Suryateja Pericherla, at present is a Research Scholar (full-time Ph.D.) in the Dept. of Computer Science & Systems Engineering at Andhra University, Visakhapatnam. Previously worked as an Associate Professor in the Dept. of CSE at Vishnu Institute of Technology, India.
He has 11+ years of teaching experience and is an individual researcher whose research interests are Cloud Computing, Internet of Things, Computer Security, Network Security and Blockchain.
He is a member of professional societies like IEEE, ACM, CSI and ISCA. He published several research papers which are indexed by SCIE, WoS, Scopus, Springer and others.

Leave a Reply