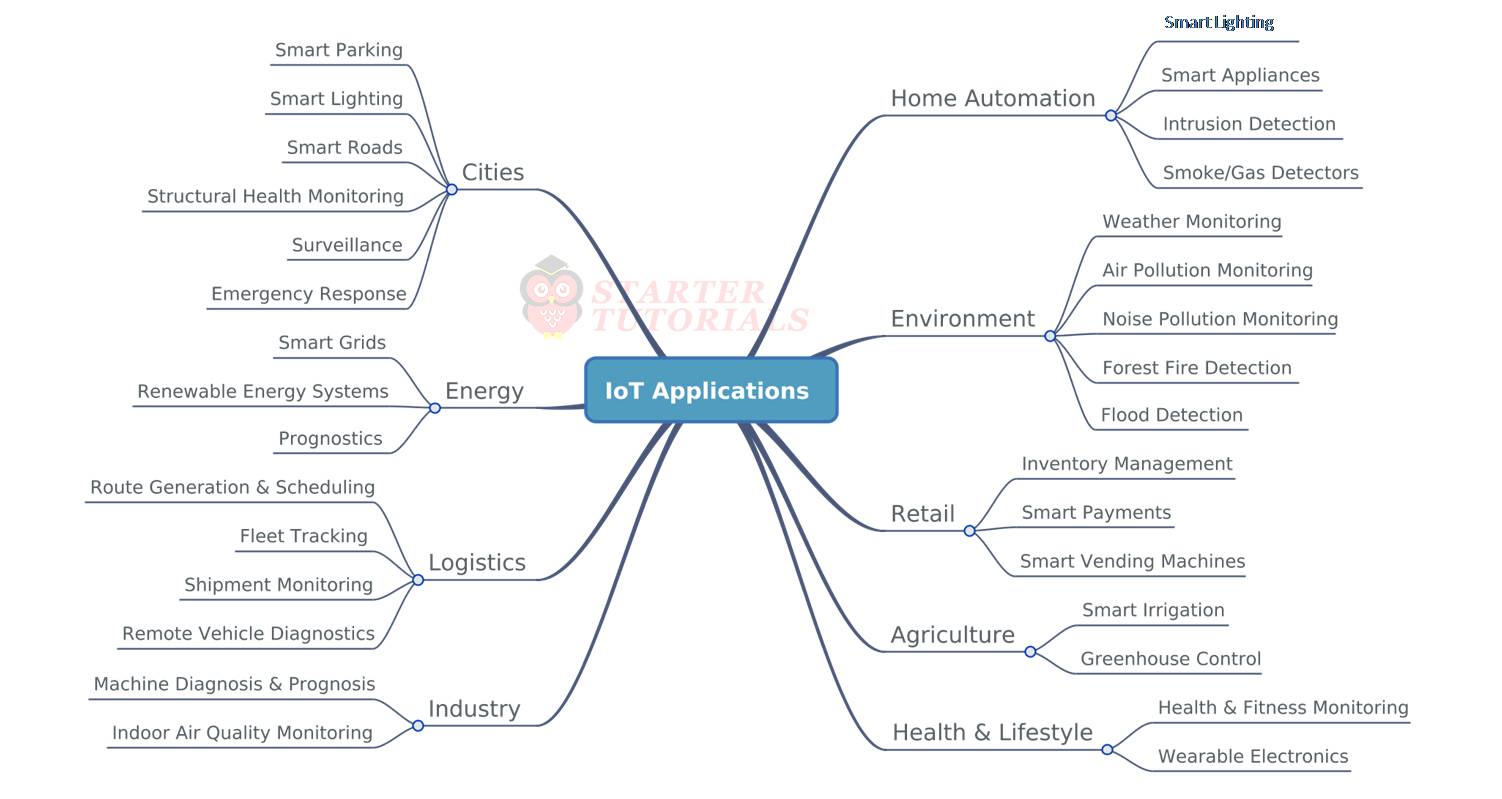
In this article we are going to learn about domain specific iot applications like smart lighting, weather monitoring, etc.
IoT applications span a wide range of domains like:
- Home Automation
- Smart Cities
- Environment
- Energy systems
- Retail
- Logistics
- Industry
- Agriculture
- Health
Watch this video to learn about iot applications in home automation, smart cities and environment domains:
Contents
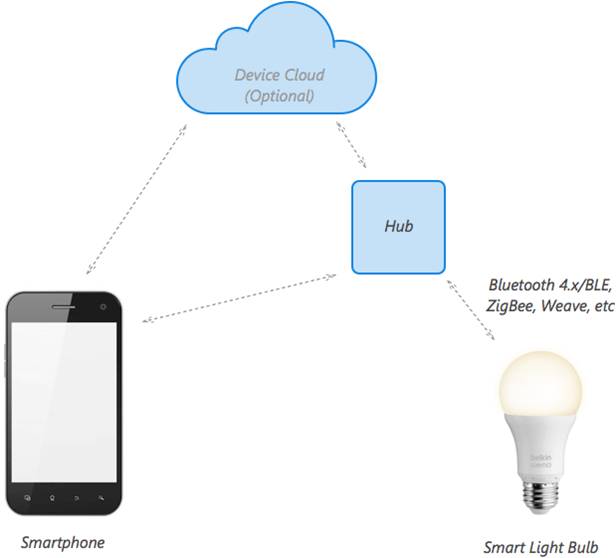
Home Automation (Smart Homes)
Sensors and actuators manage the smart home with an Internet connection. Examples of wired and wireless sensors are the security sensors, cameras, thermostats, smart plugs, lights, entertainment systems, smart plug, motion detector, door/window detector, smoke detector, energy meter, smart relay, surveillance camera, wireless speakers, LED lights, electric utility meter.
A connected home has following applications deployed in smart home:
- Mobile, tablets, IP-TV, VOIP telephony, video-conferencing, video-on-demand, video surveillance
- Home security system
- Lighting control
- Home health care
- Fire detection
- Energy efficiency
- Solar panel monitoring and control
- HVAC control
- Automated meter reading
The architecture of cloud-based IoT platform for smart home is shown in the figure below:
Smart Lighting
Smart lighting for home helps in saving the energy by adapting the lighting to the ambient conditions. Energy can be saved by sensing human movements and their environment. Wireless and Internet connected lights can be operated remotely using mobile or web application.
Smart Appliances
Smart appliances makes the management easier and also provide status information to the users remotely. For example, a smart refrigerator can keep track of items and notify the user when a item is low on stock. Examples of smart appliances are TVs, refrigerators, music systems, washing machines, etc.
Intrusion Detection
Home intrusion detection systems use cameras and sensors to detect intrusions and for raising alerts. Alerts can be sound, SMS or email sent to the user. An advanced system can even send an image or a short video clip related to the intrusion event.
Smoke/Gas Detection
Smoke detectors installed at home can detect smoke and alert the users. Smoke detectors use optical detection, ionization, or air sampling techniques to detect smoke. Gas detectors can detect harmful gases like CO or LPG. These detectors can send alerts in the form of email, SMS, or voice.
Smart Cities
The four-layer architectural framework developed by CISCO for smart cities is:
- Layer 1 consists of sensors, sensor networks, and device networks in parking lots, hospitals, streets, vehicles, banks, water supply, roads, bridges, and railroads. Protocols used at this layer are BLE, Zigbee, Wi-Fi, and NFC.
- Layer 2 captures the data at distributed computing points. Data is processed, stored, and analyzed
- Layer 3 is for central collection services, data centers, cloud and enterprise servers for data analytics
- Layer 4 consists of new innovative applications, such as, waste-containers monitoring, WSNs for power loss monitoring, smart parking, bike sharing, etc.
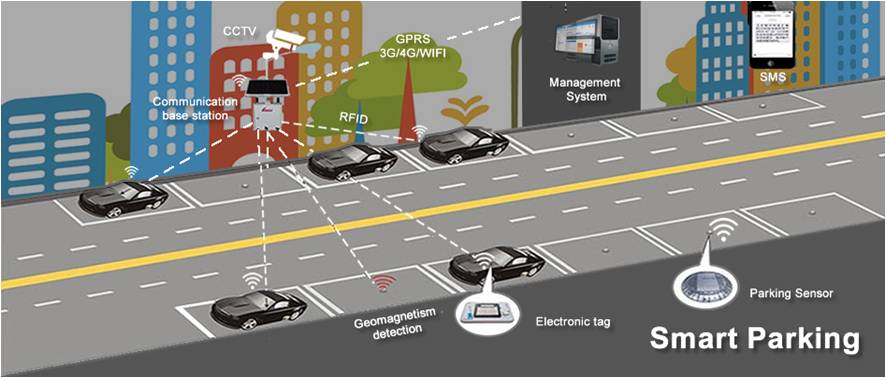
Smart Parking
Smart parking makes the search for parking space easier and convenient for drivers. In smart parking, sensors are used for each parking slot, to detect whether the slot is occupied or not. This information is aggregated by local controllers and sent over the Internet to the database. Drivers can use an application to know about empty parking slots.
Smart Lighting
Smart lighting systems for roads, parks, and buildings can help in saving energy. Smart lighting allows lighting to be dynamically controlled and also adaptive to the ambient conditions. Smart lights connected to the Internet can be controlled remotely to configure lighting intensity and lighting schedule.
Smart Roads
Smart roads equipped with sensors can alert the users about poor driving conditions, traffic congestion, and accidents. Information sensed from the roads can be sent via Internet to applications or social media. This helps in reducing traffic jams.
Structural Health Monitoring
A network of sensors are used to monitor the vibration levels in the structures. Data from the sensors is analyzed to assess the health of the structures. By analyzing the data it is possible to detect cracks, locate damages to the structures and also calculate the remaining life of the structure.
Surveillance
Surveillance of infrastructure, public transport and events in cities is required to ensure safety and security. City wide surveillance requires a large network of connected cameras. The video feeds from the cameras can be aggregated in cloud-based storage. Video analytics applications can be used to search for specific patterns in the collected feeds.
Emergency Response
IoT systems can be used to monitor buildings, gas and water pipelines, public transport and power substations. These systems provides alerts and helps in mitigating disasters. Along with cloud-based applications IoT systems helps to provide near real-time detection of adverse events.
Environment
Weather Monitoring
A smart weather monitoring system allows the following:
- Each measuring node for weather parameters is assigned an id
- Each lamp post deploys a wireless sensor node
- Each node measures the T, RH, and other parameters related to weather at assigned locations
- A group of WSNs forms a network using ZigBee
- Each network has an access point which receives data from a sensor node
- Each access point is associated with a gateway
- The information related to various weather parameters are stored on a cloud platform
- Publish weather messages to the display boards and communicate the same with s Weather API which can be accessed from mobiles and other devices
- Publish messages at real-time and send alerts using weather reporting application
- Analyse and assess the environmental impact
- Enables intelligent decisions using historical data and analytics reports
IoT-based weather monitoring systems use different sensors to gather data. That data is sent to the cloud-based storage. The collected can be analyzed and visualized with applications. Weather alerts can be subscribed by users from such applications.
Air Pollution Monitoring
A growing problem for people is the increase in air pollution from cars, toxic gases from industries like Carbon Monoxide (CO). The pollution needs monitoring and to ensure workers’ safety inside chemical plants
Sensors play a vital role in air pollution monitoring. An air monitoring system identifies chemicals, fine dust, and also measure humidity, temperature and CO2.
Air pollution monitoring system does the following:
- Monitor the levels of CO, CO2, O3, etc
- Monitor and measure levels of toxic gas such as H2S, which is a greenhouse gas
- Monitor and measure levels of hydrocarbons such as ethanol and propane
- Investigate air quality and the effects of air pollution
- Compute AQI from the parameters by averaging the values per hour or a day
- Data Visualization
- Reports the status of pollution to monitoring authorities
IoT-based air pollution monitoring systems can monitor harmful gas emissions by factories and vehicles using gaseous and meteorological sensors. The collected data can be analyzed to take decisions on pollution control approaches.
Noise Pollution Monitoring
IoT-based noise pollution monitoring systems use a number of noise pollution monitoring systems that are deployed at different places in the city. The data on noise levels from the stations is collected on servers or in the cloud. The collected data can be analyzed to generate noise maps.
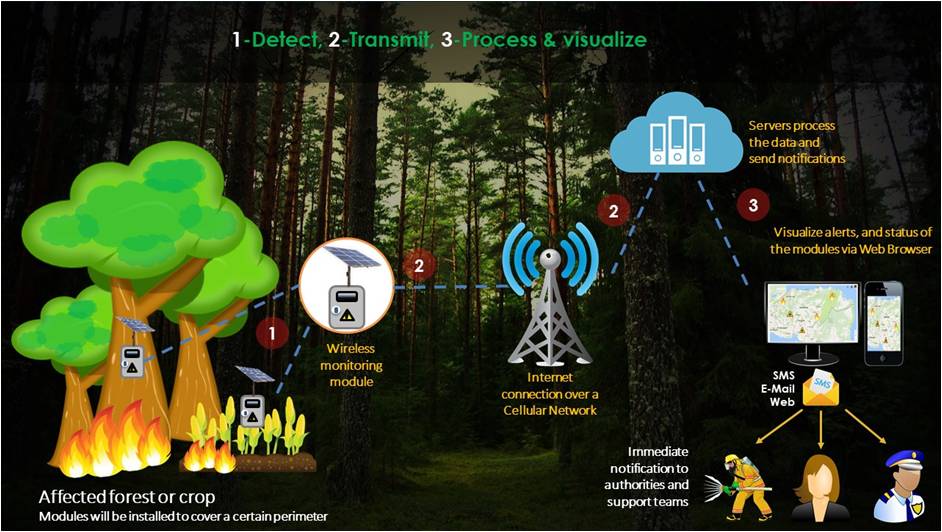
Forest Fire Detection
IoT-based forest fire detection systems use number of nodes deployed at various locations in the forest. Each monitoring node collects data about ambient conditions. This data will be collected and analyzed for the presence of fire and corresponding people will be alerted.
River Floods Detection
IoT-based flood monitor systems use number of sensor nodes to monitor the water level. Data from the sensors is aggregated on the server or in the cloud. Monitoring applications raise alerts in case of rapid increase in water level or when rapid flow rate is detected.
Watch this video to learn about IoT applications in energy, retail, logistics, agriculture, industry, health and lifestyle domains:
Energy
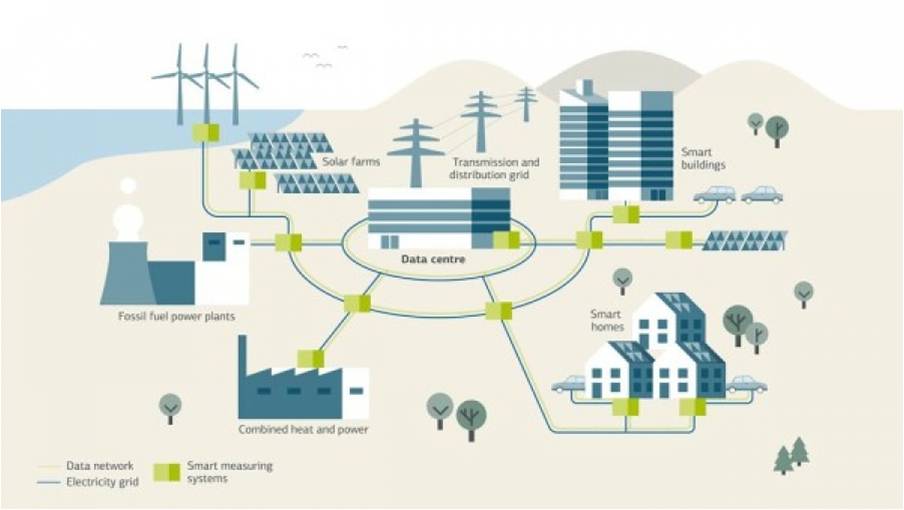
Smart Grids
Smart grid is a data communications network integrated with the electrical grid. Smart grid technology provides predictive information and recommendations to utilities, their suppliers and consumers, and how best to manage power. Smart meters can capture real-time power consumption and allows to manage power distribution remotely.
Renewable Energy Systems
Renewable energy sources (like solar and wind) produce variable output. Variable output produces local voltage swings that can impact power quality. IoT-based systems integrated with the transformers measures how much power is fed into the grid.
Prognostics
Energy systems have a large number of critical components whose health is essential for working correctly. IoT-based monitoring systems allows for the data to be gathered about these critical components. Analysis of massive amounts of data gathered by sensors can provide predictions for the impending failures.
Retail
Inventory Management
The inventory in a store or warehouse can be managed by using IoT. The products or items in the store can be attached with RFID tags. By using the RFID tags, the RFID reader or software can automatically show the number of items in the store or warehouse. If a product goes out of stock a notification can be sent to the store owner automatically.
Smart Payments
Now-a-days new types of payments are coming into picture like QR codes, NFC, contact less technologies etc. These technologies enables smart payments.
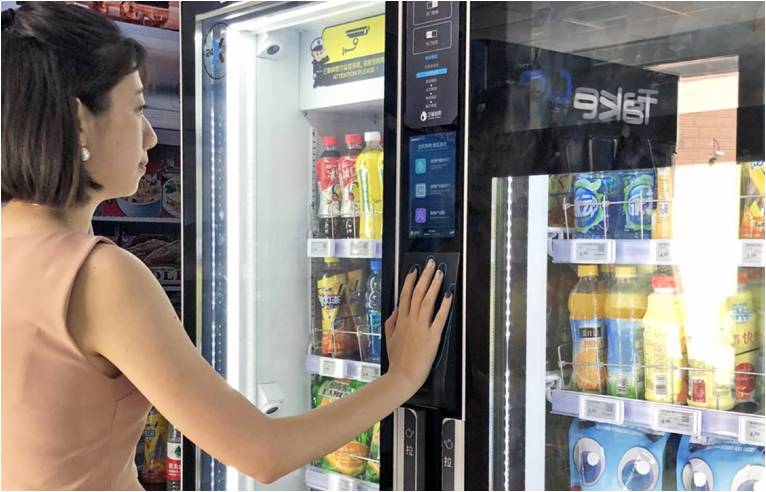
Smart Vending Machines
A smart vending machine contains several items. A consumer can insert money and get the item they want as shown in the image below. Several sensors can be attached to these vending machines such that whenever an item quantity is less, the owner of that machine will be automatically notified so that the owner can be arrangements to get that item beforehand.
Also, the vending machines can maintain the history of the consumers. So, when a consumer visits the vending machine next day, it can suggest the same item that the consumer purchased before.
Logistics
The IoT logistic applications are as follows:
- Maintaining delivery on time by vehicle tracking, safe transportation, and automation
- Connected logistics system which monitor the location of the vehicles and goods carried through those vehicles
- Sensors and devices such as RFID and IoT enable tracking of inventory items, monitoring their status and location
- Supply-chain monitoring
Route Generation and Scheduling
While delivering packages to various locations, different sensors can be fixed in those routes and they can be monitored remotely through an application. By looking at the data sent by the sensors, the delivery company can automatically know which routes are less congested and schedule the delivery of packages in such routes.
Fleet Tracking
A delivery company will have several delivery personnel working with them. Different people will use different vehicles for delivering the packages. Sensors can be fixed to those vehicles and their location can be tracked to know how long will it take to deliver the package.
Shipment Monitoring
The packages can be fixed with RFID tags or other form of remote tracking sensors to send data periodically to a server via Internet. The delivery company can use that data to track where the package is and update the user about the remaining time that will be needed to deliver the package.
Remote Vehicle Diagnostics
A vehicle rental company can fix sensors into the vehicles before giving them for rent to the customers. The company can check the data sent by the sensors to know the current location of the vehicle and easily track them.
Agriculture
Smart agriculture enables higher productivity, planning, predictions, and cost reduction.
A smart agricultural platform does the following:
- Soil analysis
- Predicting best schedule of crops
- Irrigation management
- Crop protection from pests
- Weather forecasts from satellite map data and soil analysis
- Crop-specific recommendations
- Transition to precision farming
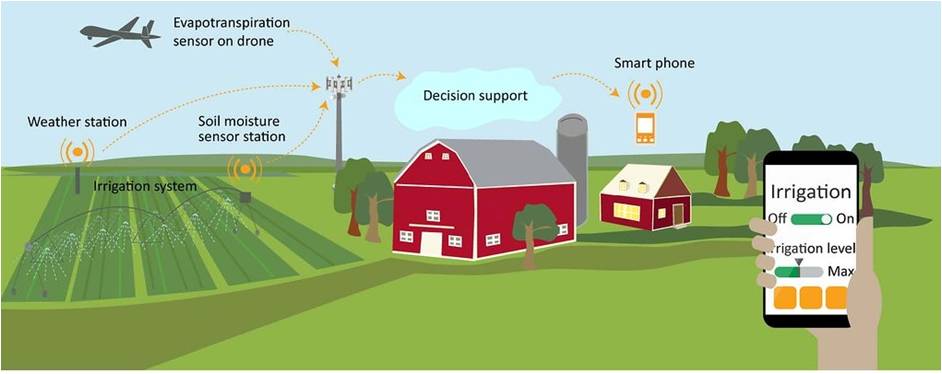
Smart Irrigation
Irrigation refers to the watering of plants. By using different sensors like temperature sensor, humidity sensor, soil moisture sensor, etc., data can be collected about the soil and the environment and let the framer know when to turn on the water sprinklers to provide water to the plants. This process is illustrated in the figure given below.
A smart irrigation system does the following:
- Sensors for moisture and actuators for watering channels are used in smart irrigation
- Soil moisture sensors with a sensor circuitry board each installed at a certain depth in soil
- Use array of actuators (solenoid valves) which are placed along the water channels
- Measures and monitors actual absorption and irrigation
- Each sensor communicates with an access point via ZigBee protocol
- An array of sensors forms a WSN
- A gateway receives the data from an access point and communicates with a cloud platform using LPWAN
- The cloud platform can be ThingSpeak, IBM Cloud, AWS, or Microsoft Azure
- Analytics at the platform analyses the moisture data and communicate to the actuators of water irrigation channels as per the water needs and past historical data
- Sensed moisture values when exceed preset threshold, triggers the alarm
- An algorithm uploads and updates the programs for the gateways and sensor nodes
- An algorithm runs at data adaptation layer and finds the faulty or inaccessible moisture sensors at periodic intervals
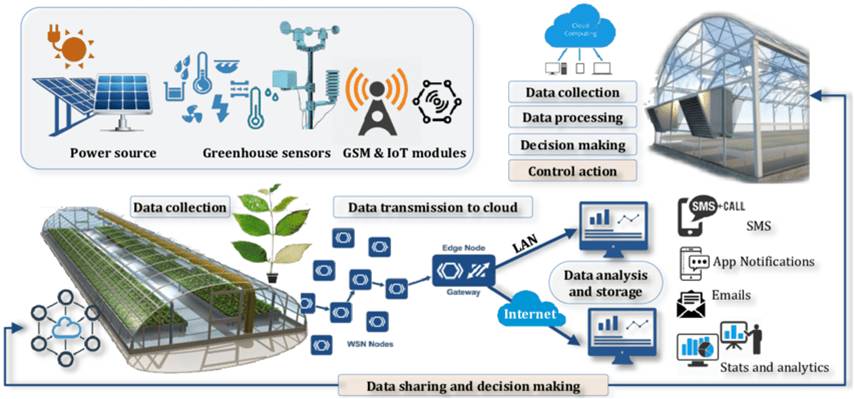
Green House Control
A green house is an artificial field that can be grown inside buildings or on the roof tops. It is a controlled environment in which several types of sensors are fixed to gather data about the soil, environment and other parameters.
The data from the green house is aggregated at a local gateway and sent to the server via Internet. The data at the server is analyzed and appropriate alerts are sent to the owner of the green house. This process is illustrated in the figure below.
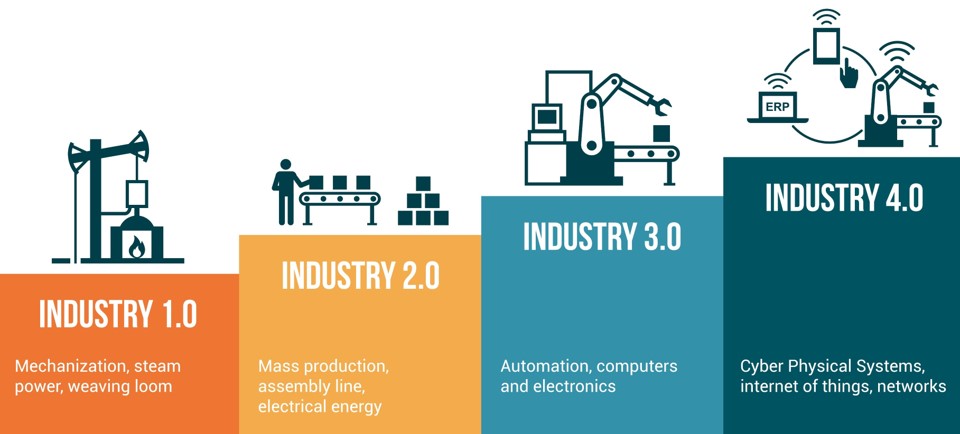
Industry
Industry 4.0 is the fourth industrial revolution. Industry 4.0 manufacturing deploys digital tools such as IoT, M2M, AI, Machine Vision, Augmented Reality, and Robotics. M2M communication between machines uses are in the production-automation and control.
- The use of IIoT is in:
- Industrial operations
- Predictive maintenance
- Increased safety
- Production planning
- Deep insight into customers (patterns and behaviour)
M2M Communication
M2M refers to the process of communication of a physical object or device at a machine with another machine of same type mostly for monitoring but also for control purposes. Each machine at an M2M system has an embedded smart device. The device senses the data or status of the machine, and performs the computations and communication functions.
A device communicates via wired or wireless systems. Machines are assigned 48-bits IPv6 addresses. The communication protocols are LWM2M (LightWeight M2M), MQTT (Message Queue Telemetry Transport), XMPP (eXtensible Messaging and Presence Protocol), etc.
M2M has many applications, for example, industrial automation, logistics, smart grid, smart cities, health, and defence. M2M initial applications were in automation and instrumentation, but now it also includes telematics applications and also IIoT (Industrial Internet of Things).
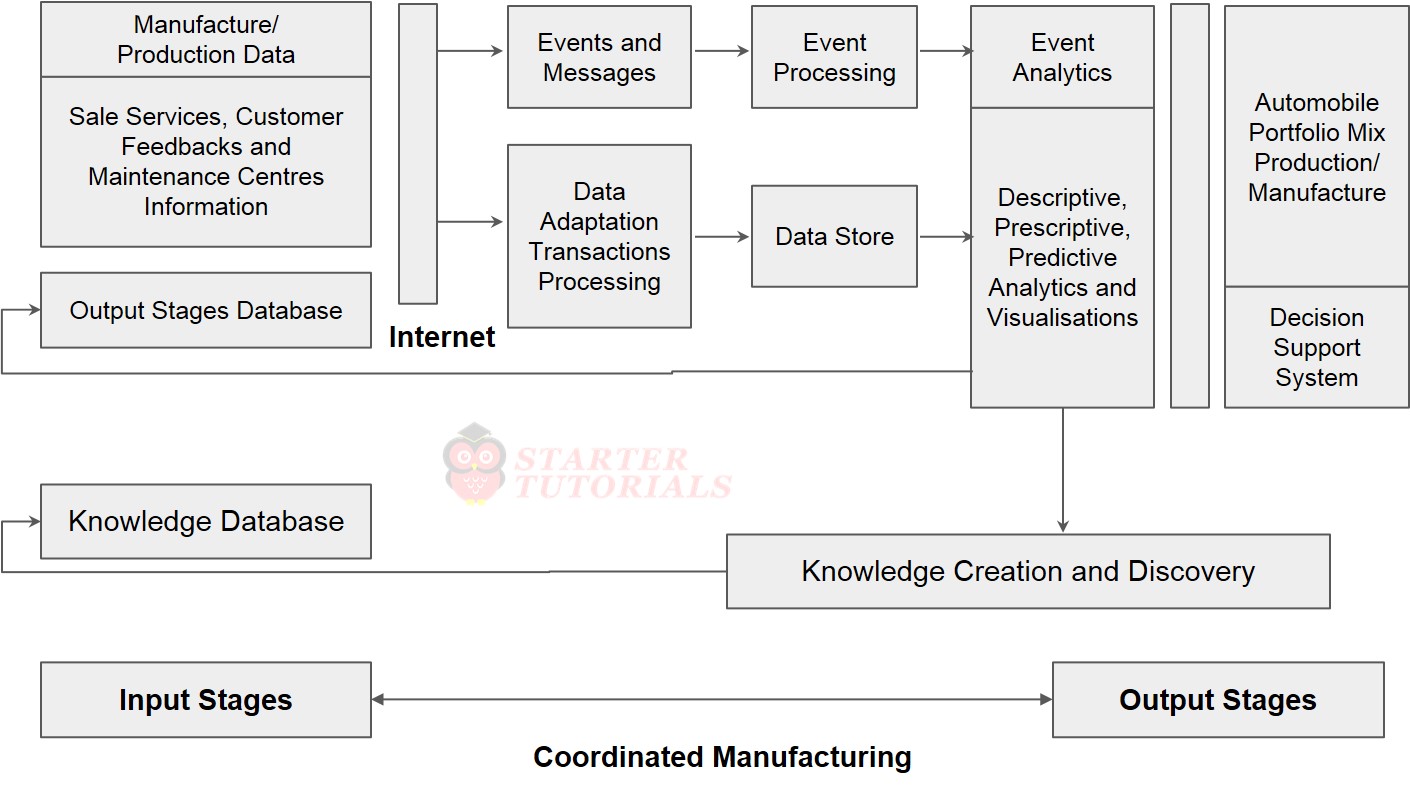
Coordinated Manufacturing
Following figure exhibits how IIoT deploys connectivity to all parts of the production process – machines, products, systems and how the machines and products communicate, and thus manage themselves using analytics and visualisation.
Machine Diagnosis & Prognosis
The machines used in the industry can be fixed with sensors. The data from the sensors can be used to diagnose the machines. We can know if the machine is working up to the expected performance or not. The data analysis will also let the owner of the machine know when the life of machine will be over.
Indoor Air Quality Monitoring
The quality of air for the working personnel inside the industry is also important. Often times leakage of dangerous gases leads to the death of industry personnel. Sensors can be fixed at different location to monitor the working environment for any leakage of hazardous gases and notify the appropriate personnel to deal with it.
Health & Lifestyle
Smart healthcare platform provides the following:
- Tracks health using health devices data and generates predictive models
- Notifies the need to take medicine and alerts for required visit to doctor
- Creates health maps with information of clinical analyses of various body regions
Health and Fitness Monitoring
With the advent of IoT remote healthcare has become an viable option for attending to patients. There is no need for patient to visit hospital for every minor health problem.
The doctor can attend to such patients from a remote location. Different sensors can be fixed on near the patient to monitor the health vitals of that patient. The data sent by the sensors is monitored by the doctor and appropriate decisions are made.
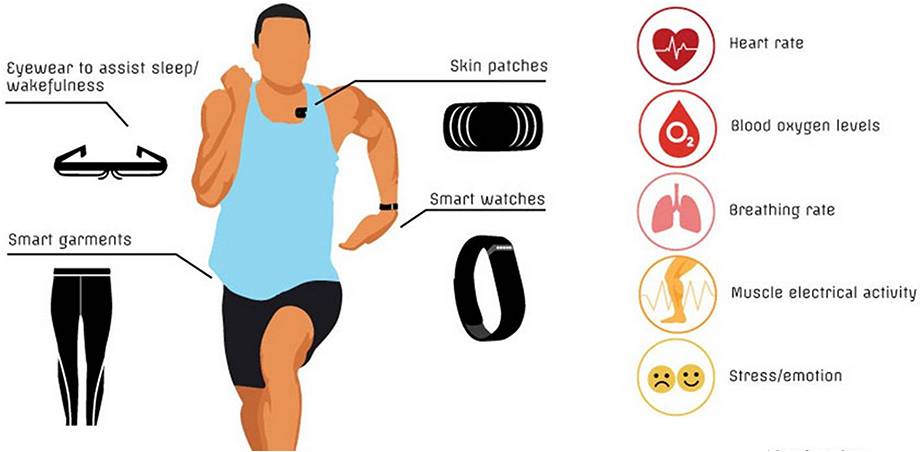
Wearable Electronics
Now-a-days there are different types of wearables available in the market to monitor health and lifestyles. Some examples of such wearables are smart watches, smart glasses, smart patches, smart garments, etc., as shown in the below figure.

Suryateja Pericherla, at present is a Research Scholar (full-time Ph.D.) in the Dept. of Computer Science & Systems Engineering at Andhra University, Visakhapatnam. Previously worked as an Associate Professor in the Dept. of CSE at Vishnu Institute of Technology, India.
He has 11+ years of teaching experience and is an individual researcher whose research interests are Cloud Computing, Internet of Things, Computer Security, Network Security and Blockchain.
He is a member of professional societies like IEEE, ACM, CSI and ISCA. He published several research papers which are indexed by SCIE, WoS, Scopus, Springer and others.








Leave a Reply