The basic idea of decentralization is to distribute the control and authority to the peripheries of an organization instead of one central body being in full control of the organization.
The benefits for organizations in following decentralization are: increased efficiency, faster decision making, better motivation, and a reduced burden on top management.
Decentralization using Blockchain
Decentralization is a core benefit and service provided by blockchain technology. By design, blockchain is a perfect vehicle for providing a platform that does not need any intermediaries and that can function with many different leaders chosen via consensus mechanisms.
This model allows anyone to compete to become the decision-making authority. A consensus mechanism governs this competition, and the most famous method is known as Proof of Work (PoW).
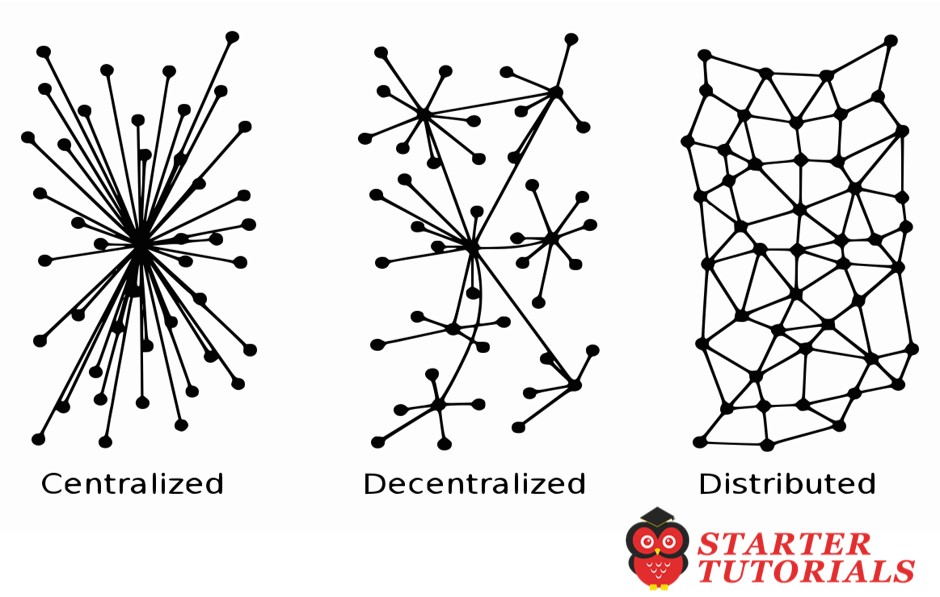
The following diagram shows the different types of systems that currently exist: central, distributed, and decentralized.
Centralized systems are conventional (client-server) IT systems in which there is a single authority that controls the system, and who is solely in charge of all operations on the system.
All users of a centralized system are dependent on a single source of service.
In a distributed system, data and computation are spread across multiple nodes in the network.
In a distributed system, computation may not happen in parallel and data is replicated across multiple nodes that users view as a single, coherent system.
The critical difference between a decentralized system and distributed system is that in a distributed system, there is still a central authority that governs the entire system, whereas in a decentralized system, no such authority exists.
A decentralized system is a type of network where nodes are not dependent on a single master node; instead, control is distributed among many nodes.
This is analogous to a model where each department in an organization is in charge of its own database server, thus taking away the power from the central server and distributing it to the sub-departments, who manage their own databases.
A significant innovation in the decentralized paradigm that has given rise to this new era of decentralization of applications is decentralized consensus.
This mechanism came into play with Bitcoin, and it enables a user to agree on something via a consensus algorithm without the need for a central, trusted third party, intermediary, or service provider.
The differences between distributed and decentralized systems can also be viewed at a practical level in the following diagrams. Below figure shows a general representation of a distributed system:
The following diagram shows a decentralized system (based on blockchain) where an exact replica of the applications and data is maintained across the entire network on each participating node:
A comparison between centralized and decentralized systems (networks/applications) is shown in the following table:
| Feature | Centralized | Decentralized |
| Ownership | Service Provider | All users |
| Architecture | Client/Server | Distributed |
| Security | Basic (not really) | More secure (not really) |
| High Availability | No | Yes |
| Fault Tolerance | Single point of failure | Highly tolerant as service is replicated |
| Collusion Resistance | Basic as it is under the control of a group or even single individual | Highly resistant as consensus algorithms ensure defense against adversaries |
| Application Architecture | Single application | Application replicated across all nodes of a network |
| Trust | Consumers have to trust the provider | No mutual trust required |
| Cost of consumer | Higher | Lower |

Suryateja Pericherla, at present is a Research Scholar (full-time Ph.D.) in the Dept. of Computer Science & Systems Engineering at Andhra University, Visakhapatnam. Previously worked as an Associate Professor in the Dept. of CSE at Vishnu Institute of Technology, India.
He has 11+ years of teaching experience and is an individual researcher whose research interests are Cloud Computing, Internet of Things, Computer Security, Network Security and Blockchain.
He is a member of professional societies like IEEE, ACM, CSI and ISCA. He published several research papers which are indexed by SCIE, WoS, Scopus, Springer and others.


Leave a Reply