In this article we will learn about cybercrime and information security along with the difference between cybersecurity and information security. We will also look at the security properties or attributes of a system or application with respect to information security.
Watch this video to learn about cybercrime and information security:
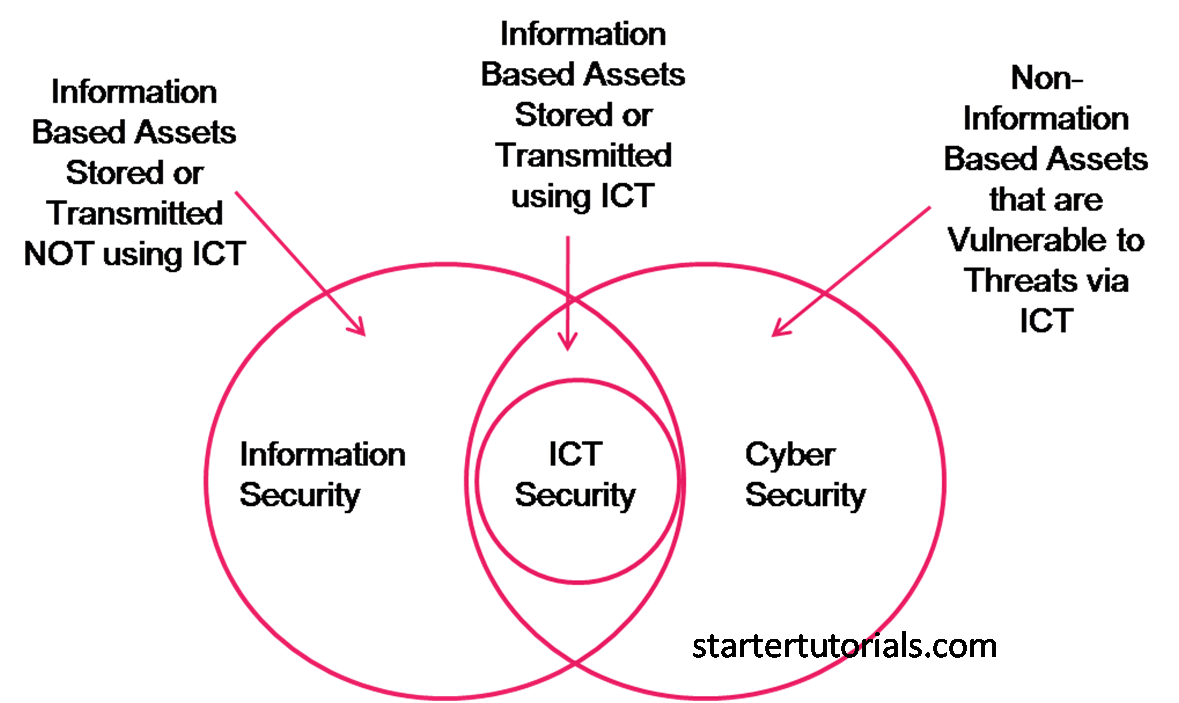
Cybersecurity can be defined as “protecting or defending the use of cyberspace from cyber attacks.”
Information security can be defined as “the protection of information and information systems from unauthorized access, use, disclosure, disruption, modification, or destruction in order to provide confidentiality, integrity, and availability.”
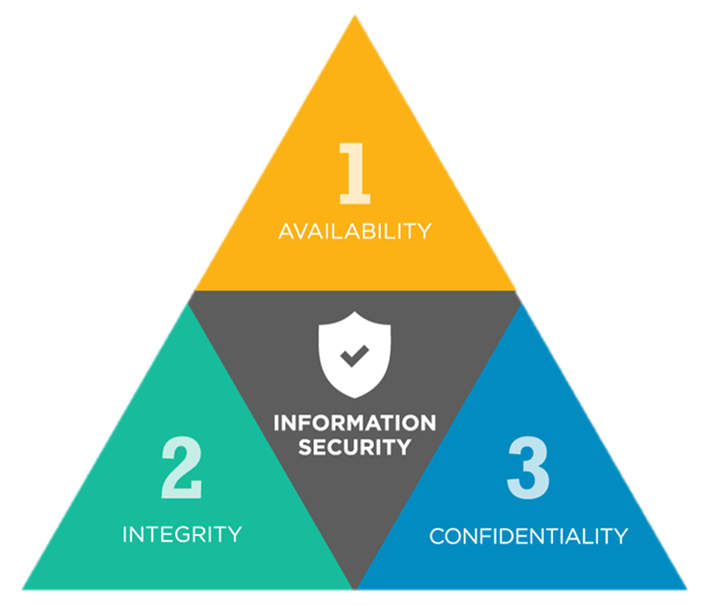
The well-known security properties or attributes are:
1. Confidentiality
2. Integrity
3. Availability
4. Authentication
5. Authorization
6. Non-repudiation
The three properties confidentiality, integrity, and availability are generally known as CIA triad or as AIC triad.
Confidentiality refers to the fact that the assets should be accessible to only authorized users. Confidentiality can be thought of as a part of privacy. Confidentiality can be implemented using encryption and decryption.
Integrity refers to the fact that the data or information either at transit or in the storage is complete and consistent i.e., it is not modified by any third party. Integrity can be implemented through hash techniques.
Availability guarantees that the application or system or assets are available for use by the authorized users. What’s the point if the assets are not available to use even if the user is genuine. Availability is implemented through backups, disaster and recovery mechanisms.
Authentication allows the identification of users. It can deduce whether a user is valid or invalid. Authentication can be implemented using passwords, biometrics, etc.
Authorization generally follows authentication. Authorization enforces access control which decides how far or up to which level has a user access to. Authorization can be implemented using access control lists etc.
Non-repudiation property ensures that a user can’t deny his/her actions against the assets. Non-repudiation can be implemented using digital signatures.
Cybersecurity can also be defined as “protecting information, equipment, devices, computer, comp-uter resources, communication devices and information stored from unauthorized access, use, dis-closure, disruption, modification or destruction.”
Quantifying the impact of cybercrime on business has some challenges. They are:
- Organization do not consider the cost of vast number of computer security incidents into their accounting.
- Difficulty in attaching a quantifiable monetary value to the corporate data.

Suryateja Pericherla, at present is a Research Scholar (full-time Ph.D.) in the Dept. of Computer Science & Systems Engineering at Andhra University, Visakhapatnam. Previously worked as an Associate Professor in the Dept. of CSE at Vishnu Institute of Technology, India.
He has 11+ years of teaching experience and is an individual researcher whose research interests are Cloud Computing, Internet of Things, Computer Security, Network Security and Blockchain.
He is a member of professional societies like IEEE, ACM, CSI and ISCA. He published several research papers which are indexed by SCIE, WoS, Scopus, Springer and others.

Leave a Reply