Blockchain is a public ledger of a timestamped, ordered, and immutable list of all transactions on the Bitcoin network.
Each block is identified by a hash in the chain and is linked to its previous block by referencing the previous block’s hash.
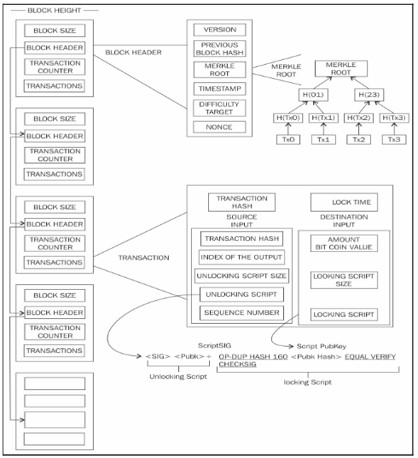
In the following table structure of a block is presented, followed by a detailed diagram that provides a detailed view of the blockchain structure.
The Structure of a Block
The following table shows the structure of a block:
| Field | Size | Description |
| Block size | 1 MB | This is the size of the block |
| Block header | 80 bytes | This includes fields from the block header |
| Transaction counter | Variable | This field contains the total number of transactions in the block, including the coinbase transaction. Size ranges from 1-9 bytes. |
| Transactions | Variable | All transaction in the block |
The Structure of a Block Header
The following table depicts the structure of a block header:
| Field | Size | Description |
| Version | 4 bytes | The block version number that dictates the block validation rules to follow |
| Previous block header hash | 32 bytes | This is a double SHA-256 hash of the previous block’s header |
| Merkle root hash | 32 bytes | This is a double SHA-256 hash of the Merkle tree of all transactions included in the block |
| Timestamp | 4 bytes | This field contains the approximate creation time of the block. More precisely, this is the time when the miner has started hashing the header. |
| Target | 4 bytes | This is the current difficulty target of the network/block |
| Nonce | 4 bytes | This is an arbitrary number that miners change repeatedly to produce a hash that is lower than the difficulty target |
As shown in the following diagram, blockchain is a chain of blocks where each block is linked to its previous block by referencing the previous block header’s hash.
This linking makes sure that no transaction can be modified unless the block that records it and all blocks that follow it are also modified.
The first block is not linked to any previous block and is known as the genesis block.
The Genesis Block
This is the first block in the Bitcoin blockchain.
The genesis block was hardcoded in the bitcoin core software.
Bitcoin provides protection against double spending by enforcing strict rules on transaction verification and via mining.
Transactions and blocks are added in the blockchain only after strict rule checking.

Suryateja Pericherla, at present is a Research Scholar (full-time Ph.D.) in the Dept. of Computer Science & Systems Engineering at Andhra University, Visakhapatnam. Previously worked as an Associate Professor in the Dept. of CSE at Vishnu Institute of Technology, India.
He has 11+ years of teaching experience and is an individual researcher whose research interests are Cloud Computing, Internet of Things, Computer Security, Network Security and Blockchain.
He is a member of professional societies like IEEE, ACM, CSI and ISCA. He published several research papers which are indexed by SCIE, WoS, Scopus, Springer and others.

Leave a Reply