Contents
Introduction
DHTML (Dynamic HTML) is not a new language. It is a combination of existing technologies like HTML, CSS, Javascript and DOM. Document Object Model (DOM) is a platform independent and language independent mechanism or API which allows the developer to implement dynamism into the web pages.
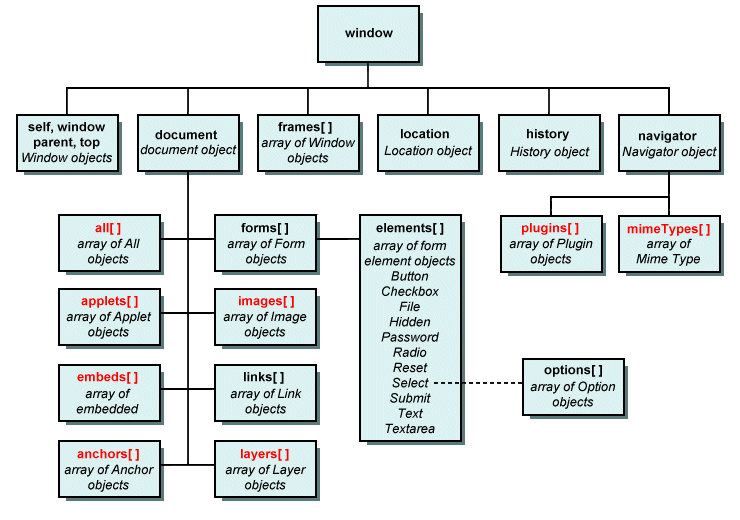
DOM represents the web page as a hierarchy of objects. The root object in the hierarchy is window. Using DOM, developers can add new elements, delete existing elements or modify the existing elements dynamically.
The DOM hierarchy is as shown below:
Accessing Elements in a Document
Different elements in a web document are treated as objects in JavaScript and each object has properties and methods. Using DOM, we can get the address of an HTML element in different ways.
First way is to use the document object’s forms array property along with the elements array property. To understand this, let’s consider the following HTML code:
<html>
<head><title>Simple form</title></head>
<body>
<form action="">
Enter your name: <input type = "text" />
</form>
</body>
</html>
To obtain the address of the textbox in the above HTML code, you can write the following code in your script:
var name = document.forms[0].elements[0].value;
The disadvantage of this method is, it becomes difficult to obtain the address of elements when there are multiple forms in a document or if there are a large number of elements in a form or if new elements are added to a form.
The second way is by using the name attribute of the HTML elements. To demonstrate this, let’s consider the following HTML code:
<html>
<head><title>Simple form</title></head>
<body>
<form action="" name="frmmain">
Enter your name: <input type = "text" name="txtname" />
</form>
</body>
</html>
To obtain the address of the textbox in the above HTML code, you can write the following code in your script:
var name = document.frmmain.txtname.value;
The problem with this method is, it doesn’t work with a group of checkboxes or a group of radio buttons which will have the same value for their name attribute. Also XHTML 1.1 does not allow name attribute on form tag.
The third way and the most commonly used method is by using the getElementById method which was introduced in DOM 1. To demonstrate this let’s consider the following HTML code:
<html>
<head><title>Simple form</title></head>
<body>
<form action="">
Enter your name: <input type = "text" id="txtname" />
</form>
</body>
</html>
To obtain the address of the textbox in the above HTML code, you can write the following code in your script:
var name = document.getElementById(“txtname”);
Since the value for id attribute can be different for checkboxes and radio buttons in a group, there will be no problems.
The id and name attributes can be used in combination for processing a group of checkboxes or radio buttons as shown below:
<form id = "genderGroup">
<input type="radio" name="gender" value="male" />Male
<input type="radio" name="gender" value="female" />Female
</form>
var count = 0;
var dom = document.getElementById("genderGroup");
for(index = 0; index < dom.gender.length; index++)
if(dom.gender[index].checked)
count++;
Below listed are various objects available in the DOM and their properties and methods:
window object
Properties on window object are:
| Property | Description |
| closed | Is a read-only Boolean property which returns true if the window opened using window.open() is closed and returns false otherwise |
| defaultStatus | Specifies the default message to be displayed on the window’s status bar when the webpage is loaded |
| name | A unique name used to reference the window |
| document | An object that contains information about the webpage loaded in the window |
| history | An object that contains the URLs visited by the user in the window |
| location | Object that contains information about the current URL |
| event | An object that contains information about the event that occurred last. It is accessible only in the event handlers |
| frames | This is an array containing references to all frames in the window |
| length | The number of frames that the window contains |
| navigator | An object that contains information about the browser application |
| screen | Refers to the screen object associated with the window |
| screenLeft, screenTop | Specifies the x and y coordinates of the window, relative to the user’s monitor screen. These properties are specific to Internet Explorer |
| self | This object is a synonym for the current window |
| top | A reference to the top-level window in the object hierarchy |
| parent | A reference to the parent window whose frameset contains the current frame |
| opener | A reference to the window from which the current window was opened using the open() method |
| status | It contains the message of the status bar of the window |
Methods on window object are:
| Method | Description |
| alert(msg) | Displays a dialog box with a specified message and an OK button |
| blur() | Removes focus from this window |
| clearInterval(ID) | Cancels a timeout that was set using the setInterval() method |
| clearTimeout(ID) | Cancels a timeout that was set using the setTimeout() method |
| close() | Closes this window |
| confirm(msg) | Displays a dialog box with a specified message and OK and Cancel buttons |
| focus() | Gives focus to this window |
| moveBy(dx, dy) | Moves this window by the specified number of pixels |
| moveTo(x, y) | Moves the top-left corner of the window to the specified screen coordinates |
| print() | Prints the contents of the window or frame |
| open(URL, [name], [features], [replace]) | Opens a new browser window |
| prompt(msg, [input]) | Displays a dialog box with a message and an input field. |
| resizeBy(dx, dy) | Resizes an entire window |
| resizeTo(x, y) | Resizes an entire window to the specified outer height and width |
| scrollBy(dx, dy) | Scrolls the viewing area of a window by the specified amount |
| scrollTo(x, y) | Scrolls the viewing area of the window to the specified coordinates |
| setInterval(func, interval, [args]) | Executes a specified function every time a specified number of milliseconds elapses |
| setTimeout(func, interval, [args]) | Executes a specified function once after a specified number of milliseconds elapses |
| stop() | Stops the current download |
Features the can be applied in the open( ) method are:
| Feature Name | Description |
| toolbar | Whether the toolbar should be present or not. Default is yes. |
| titlebar | Whether the titlebar should be present or not. Default is yes. |
| status | Status bar should be present or not. Default is yes. |
| scrollbars | Window should have scrollbars or not. Default is yes. |
| resizable | Window can be resized or not. Default is yes. |
| menubar | Menubar should be present or not. Default is yes. |
| location | Window contains an address bar or not. Default is yes. |
| directories | Directory buttons should be present or not. Default is yes. |
| channelmode | Should be displayed in theater mode or not. Default is no. |
| fullscreen | Display in full-screen mode or not. Default is no. |
location object
Properties on location object are:
| Property | Description |
| href | Refers the entire URL |
| hostname | URL host section |
| host | URL’s hostname and port section |
| port | URL’s port section |
| pathname | URL’s pathname section |
| search | URL’s query string portion |
| protocol | URL protocol name including “:” |
| hash | URL anchor |
Methods on location object are:
| Method | Description |
| reload() | Current URL is reloaded. This is equal to refresh button on the browser. The argument true ignores browser cache and reloads |
| replace(URL) | Loads the specified URL by replacing the current one. Does not affect the browser’s history |
history object
Properties on history object are:
| Property | Description |
| current | Current webpage URL (Netscape only) |
| length | Number of entries of the history object |
| next | Next URL in the history object (Netscape only) |
| previous | Previous URL in the history object (Netscape only) |
Methods on history object are:
| Method | Description |
| back() | Loads previous URL in the history list |
| forward() | Loads next URL in the history list |
| Go(relPos | string) | Loads a specific URL in the history list. The relPos indicates number of places to go, relative to the current position. String argument indicates the specific URL to be loaded. |
Properties on navigator object are:
| Property | Description |
| appCode | Code name of the browser |
| appName | Name of the browser |
| appMinorVersion | Minor version number of the browser |
| cpuClass | Type of CPU |
| platform | OS name |
| plugins | Array of plugins installed in the browser |
| systemLanguage | Language being used by the system (en-us) (IE only) |
| userLanguage | Language the user is using (en-us) (IE only) |
| appVersion | Version of the browser |
| userAgent | Information about the browser added in the HTTP header |
| onLine | Boolean value of true or false |
| cookieEnabled | Specifies whether cookies are enabled or not |
| mimeTypes | Array of MIME types supported by the browser (NS and firefox only) |
Methods on navigator object are:
| Method | Description |
| javaEnabled() | Indicates whether the browser supports javascript or not |
| taintEnabled() | Indicates whether the browser supports taint (a security protection mechanism for data) or not |

Suryateja Pericherla, at present is a Research Scholar (full-time Ph.D.) in the Dept. of Computer Science & Systems Engineering at Andhra University, Visakhapatnam. Previously worked as an Associate Professor in the Dept. of CSE at Vishnu Institute of Technology, India.
He has 11+ years of teaching experience and is an individual researcher whose research interests are Cloud Computing, Internet of Things, Computer Security, Network Security and Blockchain.
He is a member of professional societies like IEEE, ACM, CSI and ISCA. He published several research papers which are indexed by SCIE, WoS, Scopus, Springer and others.

Leave a Reply