In this article we will learn about the history of computers. I hope you have already learned about basic software concepts.
Before going to start reading this article, see our complete C programming tutorial for beginners.
We will start with the classification of the history of computers into various generations and then look at each generation in detail.
Before going to learn about different generations of computers, have a look at historical computing devices in the below video.
Watch this video to learn about different generations of computers:
The history of computers is often referred to in terms of five distinct eras/generations. Each generation is characterized by major technological development that fundamentally changed the way computers operate, resulting in increasingly: smaller, cheaper, more powerful and more efficient devices. The five generations are:
- First Generation (1946 to 1955)
- Second Generation (1956 to 1963)
- Third Generation (1964 to 1970)
- Fourth Generation (1971 to 1991)
- Fifth Generation (1992 to Present)
Contents
First Generation Computers
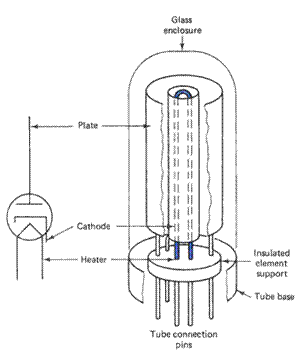
The first generation computers used vacuum tubes which are large in size. The size of first generation computers was usually very large which occupied an entire room in a building.
These computers were very expensive and were limited in memory. Also these computers generated a lot of heat. The language used for programming was machine language. UNIVAC is a famous example for first generation computer. A vacuum tube is as shown below:
Second Generation Computers
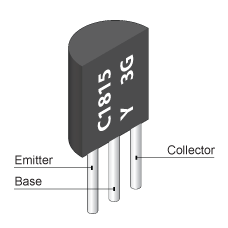
In the second generation computers, vacuum tubes are replaced by electronic component called transistor. Transistors are small in size when compared to vacuum tubes.
So, the second generation computers are still huge but smaller when compared to first generation computers. Heat generation was still high. Assembly languages were used for programming. A transistor is as shown below:
Third Generation Computers
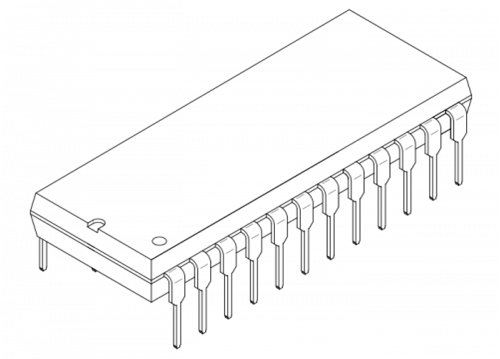
In third generation computers, new electronic components called integrated circuits (IC) were used. Generally these ICs consist of thousands of transistors along with other electronic components embedded onto a single electronic circuit board by using technology called Large Scale Integration (LSI).
Third generation computer were smaller when compared to previous generation computers. They were fast and efficient. High-Level languages were used for programming. An integrated circuit chip is as shown below:
Fourth Generation Computers
In fourth generation computers, ICs were replaced by microprocessors which consist of millions of transistors along with other electronic devices.
These microprocessors were made by using Very Large Scale Integration (VLSI) technology. These computers are powerful, smaller and cheaper when compared to previous generation computers. A microprocessor is as shown below:
Fifth Generation Computers
The fifth generation is not declared officially yet. The fifth generation is not characterized by the change is hardware technology rather it is the change in computer usage. Fifth generation computers depend on the concept called Artificial Intelligence (AI) which enables the computer to behave like a human.
Watch this video to learn about historical computing devices:
Now, let’s learn about basic networking concepts.

Suryateja Pericherla, at present is a Research Scholar (full-time Ph.D.) in the Dept. of Computer Science & Systems Engineering at Andhra University, Visakhapatnam. Previously worked as an Associate Professor in the Dept. of CSE at Vishnu Institute of Technology, India.
He has 11+ years of teaching experience and is an individual researcher whose research interests are Cloud Computing, Internet of Things, Computer Security, Network Security and Blockchain.
He is a member of professional societies like IEEE, ACM, CSI and ISCA. He published several research papers which are indexed by SCIE, WoS, Scopus, Springer and others.


i like ur contains writing